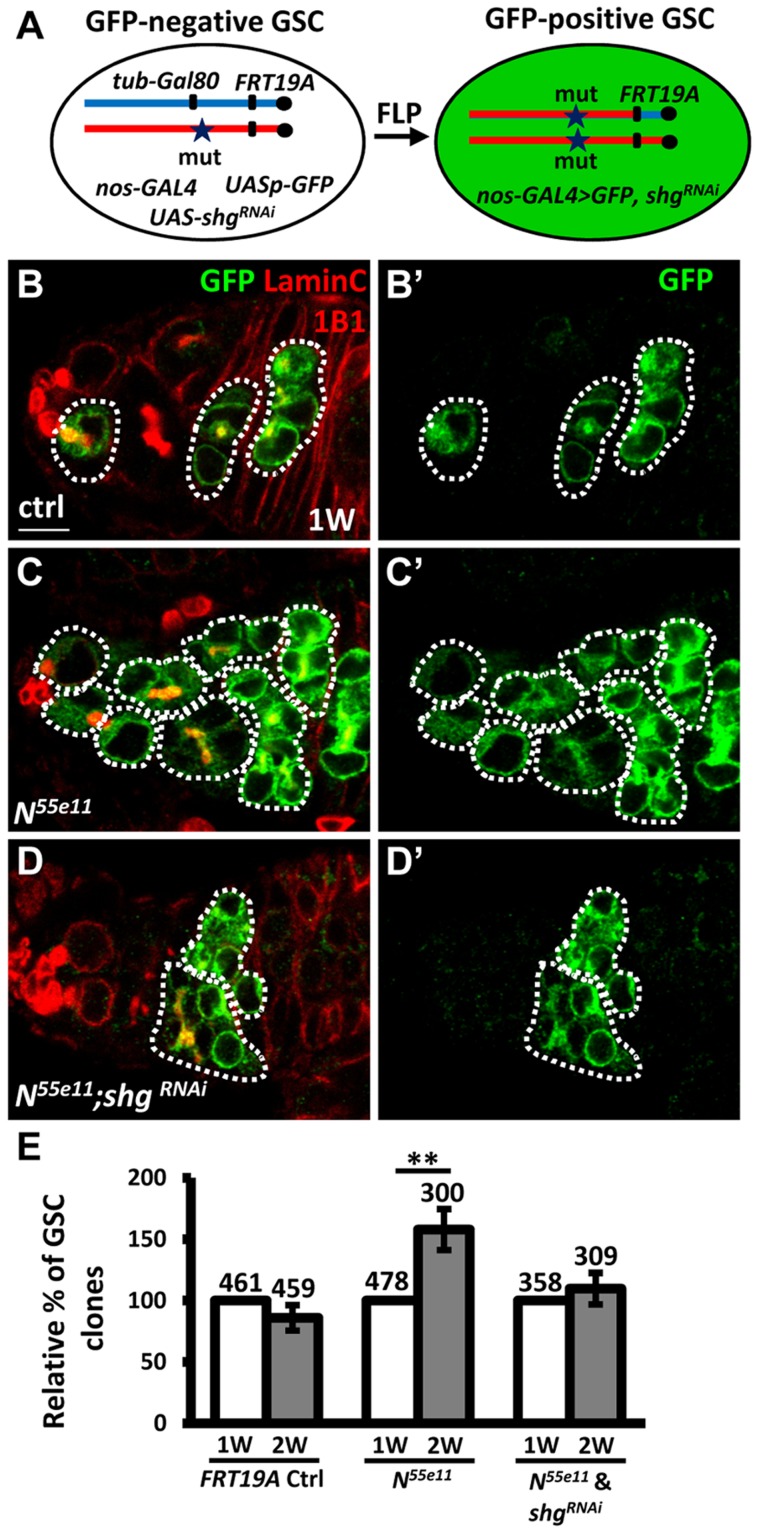
Figure 4. Notch signaling controls GSC-niche adhesion via E-cadherin.
(A) Mitotic recombination was used to generate GSCs lacking N and Gal80 (Gal80 suppresses GAL4 expression). Females carried a wild-type (wt) allele linked to a tub-GAL80 transgene in trans with an N mutant (mut) allele on one X chromosome, and non-GAL4, UASp-mCD8GFP, and UAS-shgRNAi on the third chromosome. FLP-mediated recombination between FRT sites during mitotic division generated an N homozygous mutant cell lacking GAL80 (identifiable by the presence of GFP expression), which enabled transcription of GFP and shgRNAi via the binding of GAL4 onto UAS elements. (B–D) One-week (w)-old mosaic germaria with GFP (green, mutant cells), 1B1 (red, GSC fusomes), and LamC (red, cap cell nuclear envelopes) labels. GFP-positive (+) GSCs and their daughter cells are outlined by dashed lines. Control (ctrl) germarium (B) contains one wt and one GFP+ GSC and their progeny, N55e11 mutant germarium (C) contains two GFP+ GSCs (full GSC clone) and their progeny, while shgRNAi-knock down N55e11 mutant germarium (D) contain no GFP+ GSCs, but do contain their progeny, indicating that GFP+ GSCs have been lost from the niche. B′-D′ show the GFP channel only. Scale bar: 5 µm. (E) Relative percentage of GSC clones (as a proportion of total GSCs) at 1 and 2w after clone induction. The number of mosaic germaria analyzed is shown above each bar. **, P<0.01. Error bar, mean ± SEM. The genotype of the control germaria is hs-flpneoFRT19A/GAL80FRT19A.