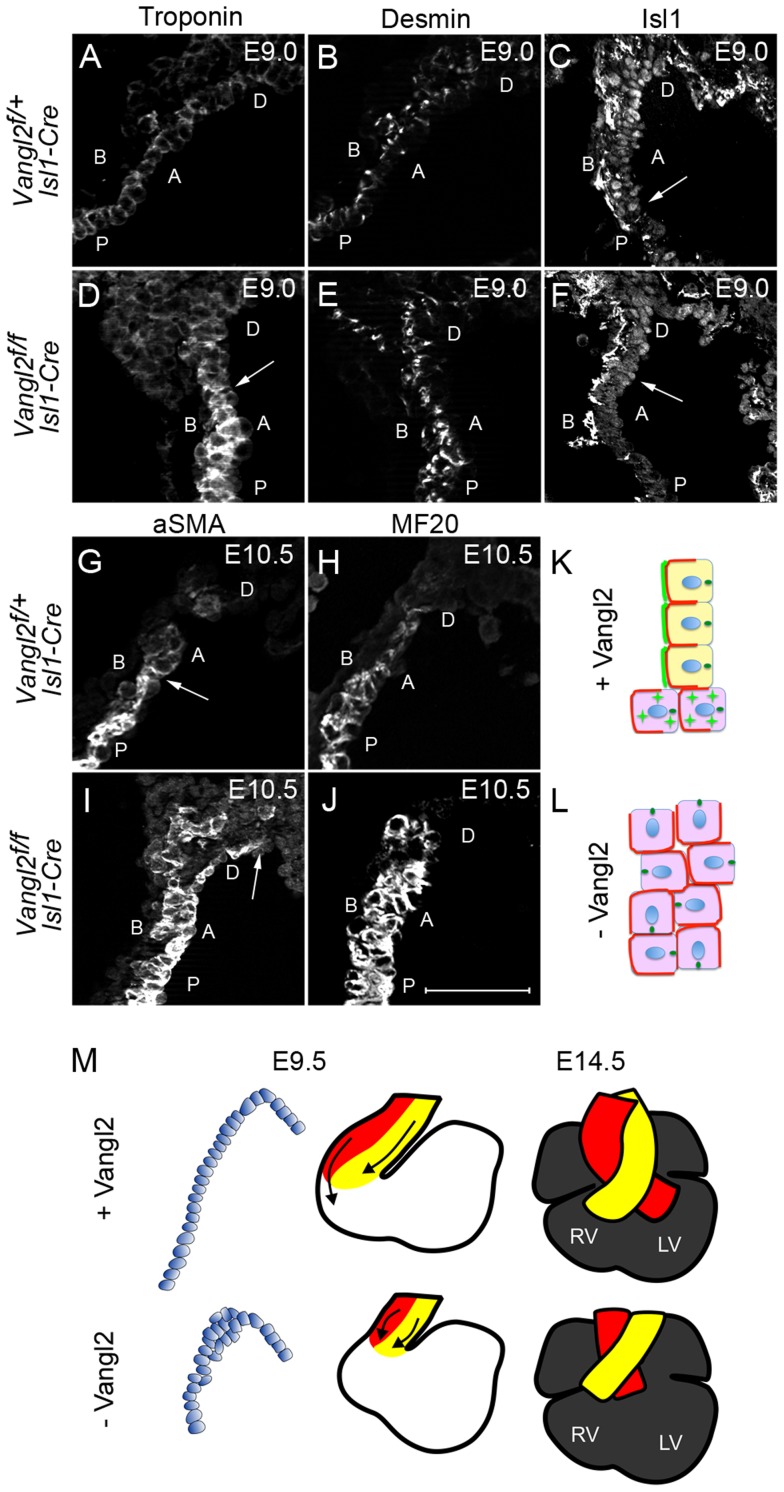
Figure 8. Loss of Vangl2 results in loss of SHF progenitor phenotype and premature differentiation in the distal outflow tract of Vangl2flox/flox; Isl1-Cre embryos.
A–F) At E9.0, cardiac troponin I expression is low distally and increases proximally through the outflow tract of control embryos (A). In contrast, high-level expression is found more distally in Vangl2flox/flox; Isl1-Cre embryos (D, n = 2). Desmin, which is expressed at high level in cardiomyocytes and at lower level by smooth muscle cells (B) is also increased within the distal outflow tract of Vangl2flox/flox; Isl1-Cre embryos (E, n = 3). Whereas Isl1 is localised to the nucleus of control embryos throughout an extended region of the distal outflow tract, defining the transition zone (C - arrows), it is significantly reduced in the nuclei of cells in the distal outflow of Vangl2flox/flox; Isl1-Cre embryos (F – arrows point to the proximal extent of the staining, n = 3). G–J) Similar to E9.0, at E10.5, both αSMA (G,I, n = 3) and MF20 (H,J; staining myosin heavy chain, n = 3) are expressed more distally in the outflow tract of Vangl2flox/flox; Isl1-Cre embryos than in stage-matched littermates. K,L) Cartoon showing distribution of Vangl2 (bright green) at the boundary of the transition zone in the distal outflow tract of control embryos, where it is localised to the membrane through the transition zone, but is cytoplasmic (green stars) more proximally. Basolateral markers are represented in red and the MTOC, localising to the apical side of the cell, in dark green (K). In the absence of Vangl2, basolateral marker domains are expanded and the MTOC, although still apically positioned, is rotated in many cells. The wall is also thickened (L). M) Model showing how loss of epithelial phenotype of the cells within the distal outflow tract wall at E9.5 could result in a shortened outflow tract and double outlet right ventricle by E14.5. A = Apical, B = Basal, D = distal, P = proximal, Vangl2f = Vangl2flox. Scale bar = 100 µm.