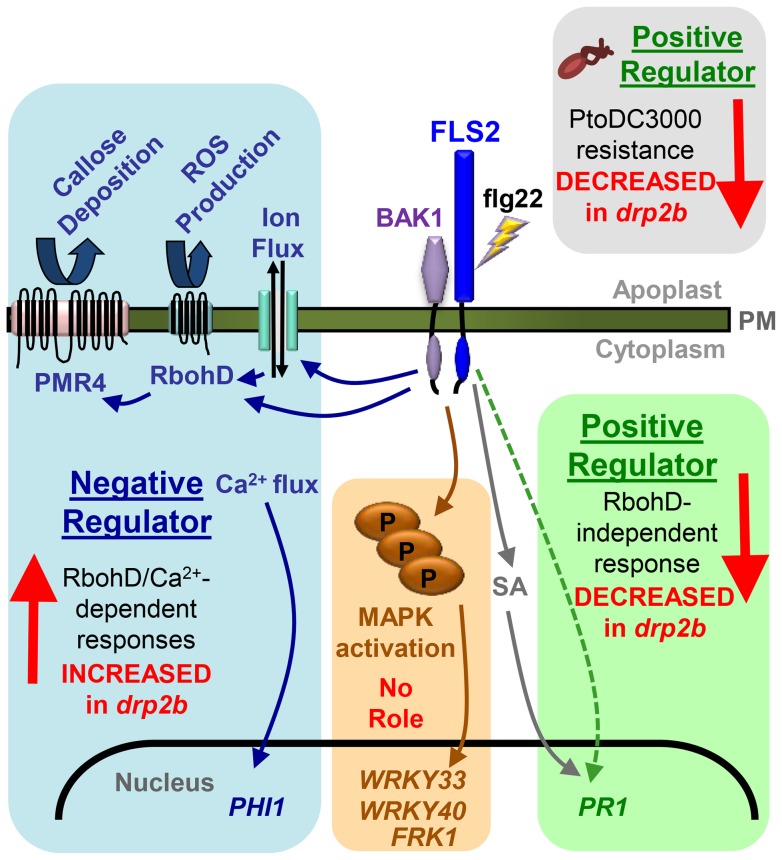
Figure 8. Summary of non-canonical response defects in drp2b within the different branches of the flg22-signaling network.
Flg22-binding to FLS2 and its co-receptor BAK1 initiates at least three distinct branches of flg22-signaling networks that are differentially affected by loss of DRP2B compared to wildtype plants. All tested RbohD/Ca2+-dependent responses are increased in drp2b plants (blue box) consistent with DRP2's function as a negative regulator of these responses. Loss of DRP2B has no effect upon flg22-induced MAPK pathway activation (brown box) implying that DRP2B has no apparent role in the MAPK pathway. However, drp2b displays decreased PR1 mRNA expression in response to flg22, which occurs independently of RbohD (green box) and may be at least in part, independent of SA. Correlating with decreased transcription of PR1, drp2b plants show decreased resistance to bacterial pathogen infection (Pto DC3000) (gray box) indicating that DRP2B is a positive regulator of resistance to this bacterial strain. The non-canonical combination of phenotypic defects observed in drp2b may be in part due to altered vesicular trafficking of FLS2 and potentially other yet unknown PM-resident cargo proteins. For simplicity, not all known components of the flg22-signaling network are included in this model.