Figure 2.
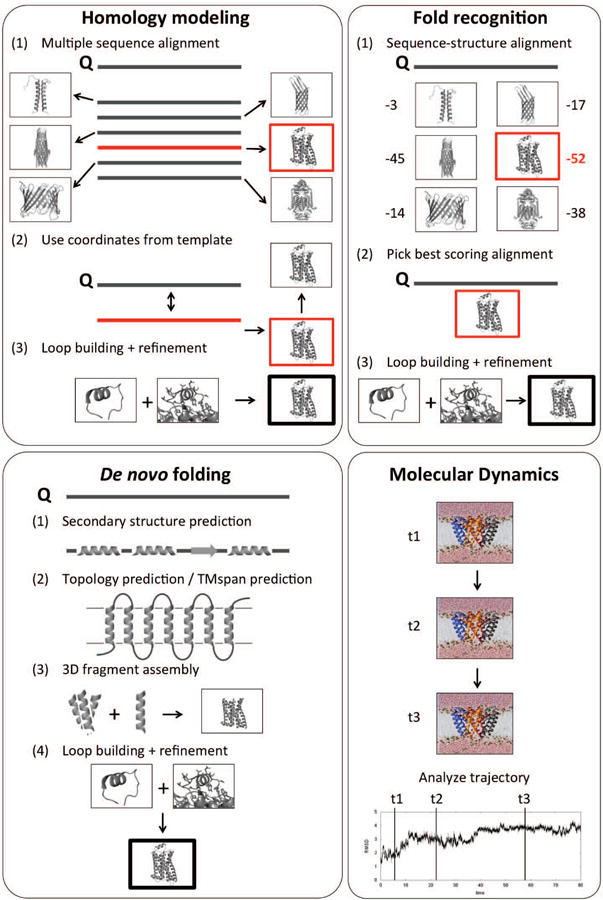
Methods for predicting 3D protein structures. (Top left) Homology modeling requires a template to be found by multiple sequence alignment to the query sequence (Q). (Top right) Fold-recognition is used for low sequence similarities that prevent template identification solely based on multiple sequence alignments. A sequence-structure alignment of the query sequence with a database of structures and subsequent scoring is necessary to identify a suitable template. (Bottom left) De novo (or ab initio) folding is used when no template is available and/or for novel protein folds. (Bottom right) MD simulations are currently unable to fold proteins larger than ∼80 residues, they are used to study dynamics and molecular processes of proteins along a time trajectory.
