Figure 4.
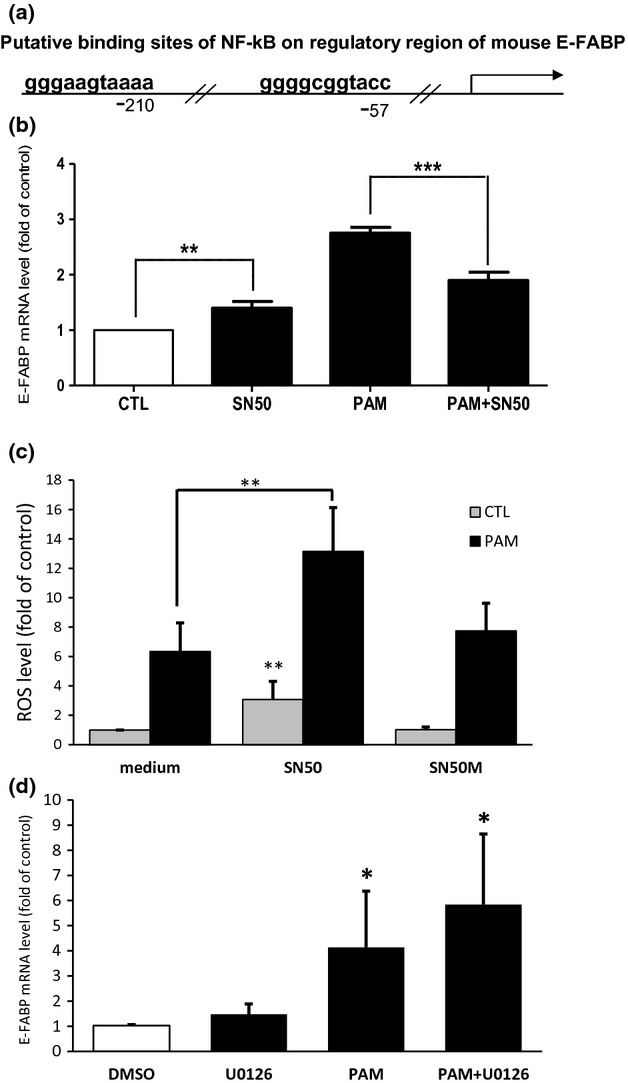
NF-ĸB inhibitor affects palmitic acid-induced lipotoxicity (PAM-LTx)-induced epidermal fatty acid-binding protein (E-FABP) expression and reactive oxygen species (ROS) accumulation in NGFDPC12 cells. (a) The putative binding sites of NF-kB on regulatory region of mouse E-FABP predicted by PROMO program (Farre et al. 2003). (b) Cells were treated with control medium (CTL), NF-kB inhibitor SN50 at 50 μg/mL in control medium (SN50), 300 μM PAM (PAM) or PAM together with SN50 (PAM+SN50) for 12 h and E-FABP mRNA levels were determined by real-time RT-PCR. (c) Cells were treated with control medium, SN50, or control peptide SN50M with or without 300 μM PAM for 18 h and ROS level was measured with H2DCFDA method. (d) Cells were treated with 20 μM of U0126 or control medium with 0.1% DMSO with or without 300 μM PAM for 12 h and E-FABP mRNA levels were determined by real-time RT-PCR. The data represent mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. Significance symbols: *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001. Significance symbols are shown above bars when compared to control group and are shown above lines when compared between two linked groups.
