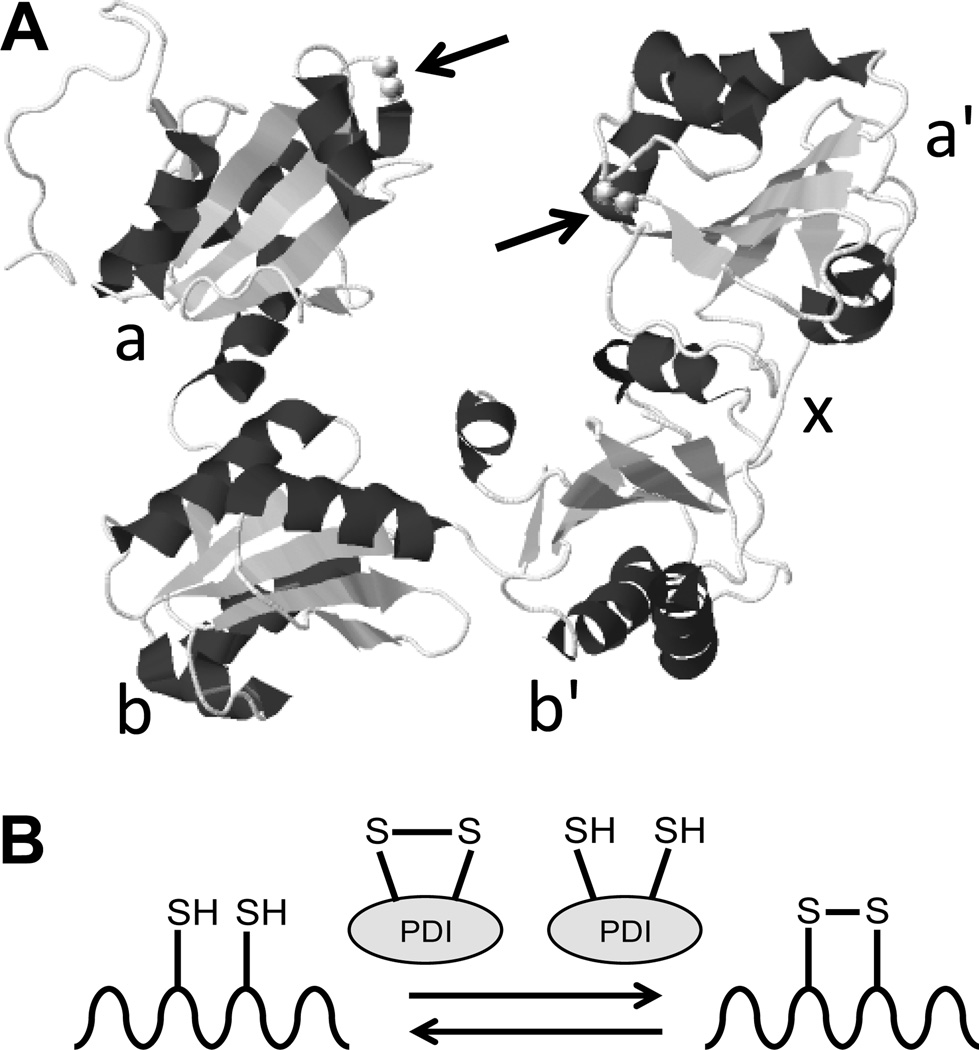
Figure 1. Structure and function of protein disulfide isomerase.
A, The structure of protein disulfide isomerase (PDI) as determined by x-ray crystallography. The a, b, b', x, and a' domains are indicated. Arrows denote the location of the CGHC catalytic motifs (adapted from Wang et al., Antioxid. Redox Signal., 2013).3 B, The primary function of the CGHC motifs is to catalyze the oxidation and reduction of disulfide bonds to facilitate proper folding of proteins as they are synthesized in the endoplasmic reticulum. However, PDI can also be secreted from vascular cells and extracellular PDI is essential for thrombus formation.