Figure 6.
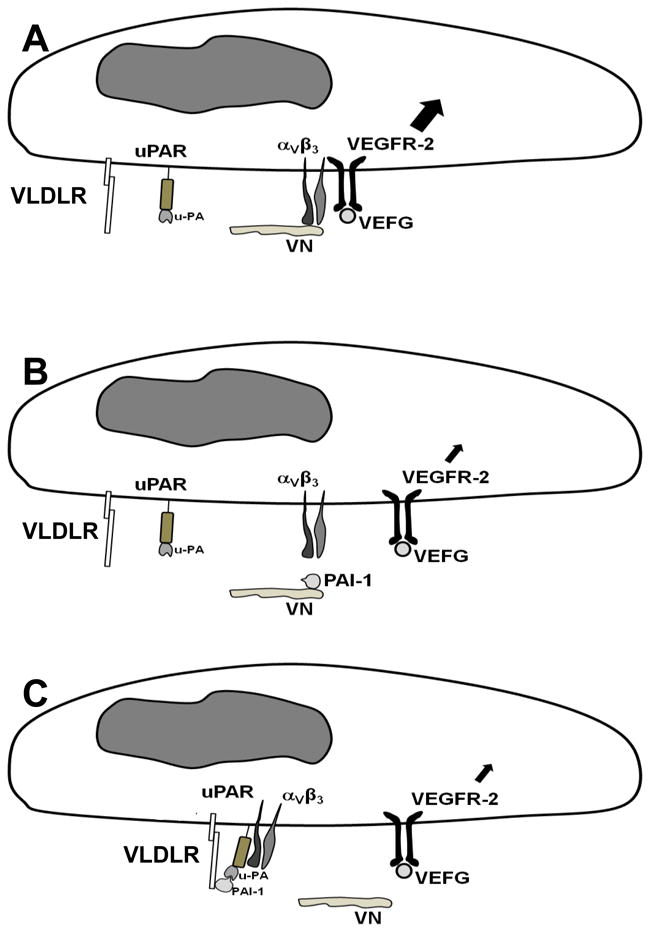
Proposed model by which PAI-1 inhibits VEGF signaling. (A) VEGF induces strong angiogenic signaling (large intracellular arrow) when αVβ3 is bound to VN and VEGFR-2. (B) PAI-1 binds VN and competitively blocks binding of αVβ3, which uncouples the pro-angiogenic binding interaction between αVβ3 and VEGFR-2 and down-regulates VEGF signaling (small intracellular arrow). (C) PAI-1-uPA complex binds to VLDLR and uPAR, which, through a uPAR-αVβ3 binding interaction, triggers dissociation of αVβ3 from VN, thereby uncoupling the pro-angiogenic binding interaction between αVβ3 and VEGFR-2, which down-regulates VEGF signaling.
