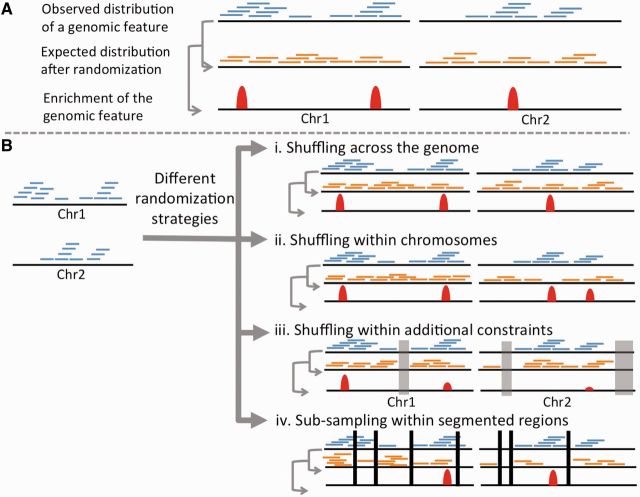
Figure 1:
(A) The basic principle behind permutation analysis to determine genome-wide enrichment of a genomic or epigenomic feature. (B) A different randomization strategy can produce a different expected distribution, and hence affect statistical significance of enrichment of the feature. In (Biii), disallowed regions are masked (gray) while shuffling with additional constraints. The displayed list does not represent the exhaustive list of possible randomization strategies. A colour version of this figure is available at BIB online: http://bib.oxfordjournals.org.