FIG. 1.
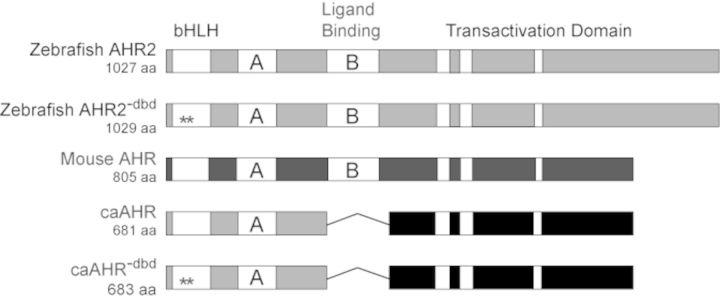
Construction of a zebrafish caAHR. Schematics of zebrafish AHR2 and mouse AHR (Ahb1) are shown with domains depicted. PAS A and PAS B domains indicated as A and B; the white bars within the transactivation domains indicate conserved acidic and Q-rich regions. The asterisks indicate Gly-Ser insertions between residues R38 and D39 in the bHLH region to make the DNA-binding mutant control constructs, AHR2−dbd and caAHR−dbd. The fusion of the caAHR chimera consisting of the amino terminus of zebrafish AHR2 (amino acids 1–298) fused to the transactivation domain of the mouse AHR (amino acids 422–805) is shown, with deletion of the PAS B region indicated by a line.
