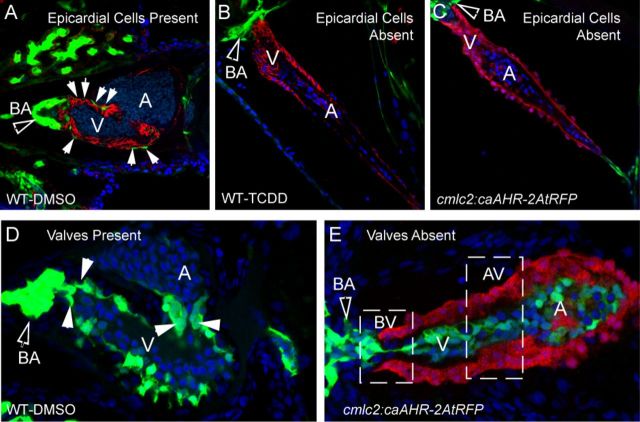
FIG. 8.
Effect of caAHR expression in cardiomyocytes on epicardium, BA, and valve development. (A–C) Transgenic caAHR founders (cmlc2:caAHR-2AtRFP) or wild-type controls (AB) were crossed with Tg(pard3:EGFP) reporter fish marking the epicardial cells. (A) Wild-type x Tg(pard3:EGFP) offspring treated with DMSO, (B) wild-type x Tg(pard3:EGFP) treated with TCDD as described in the Materials and Methods. Embryos were collected and stained with antibodies against ALCAM (red) and stained with DAPI (blue), and representative images are shown, n = 7; 120 hpf. (C) Offspring of cmlc2:caAHR-2AtRFP founder crossed with Tg(pard3:EGFP) reporter fish. caAHR expression in the myocardium is indicated by the red RFP signal; epicardial and BA cells are green. The filled arrows indicate the BA; white solid arrows indicate normal epicardial cells. (D–E) Wild-type (AB) or transgenic caAHR founders (cmlc2:caAHR-2AtRFP) were crossed with Tg(flk1:EGFP) reporter fish. (D) Wild-type x Tg(flk1:EGFP) offspring. (E) Offspring of cmlc2:caAHR-2AtRFP founder crossed with Tg(flk1:EGFP) reporter fish. The filled arrows indicate the BA; white solid arrows indicate normal valve cushions. n = 7; 96 hpf.