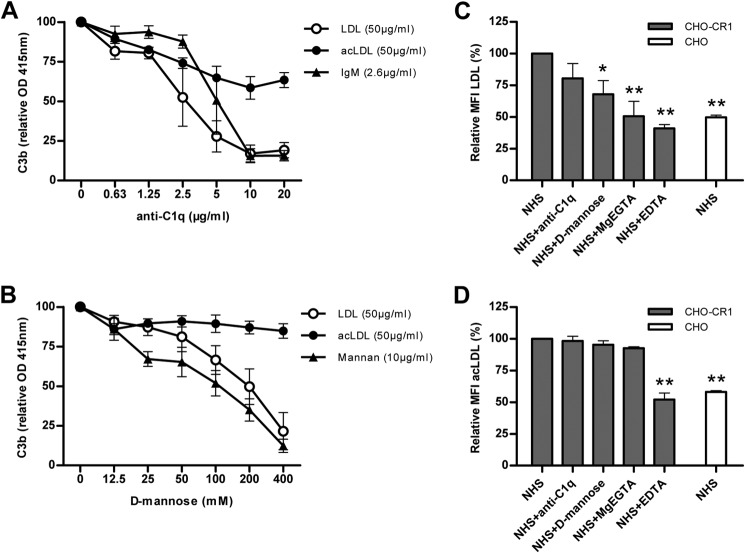
FIGURE 5.
C3b opsonization of LDL was highly reduced by the addition of anti-C1q to 10% NHS, whereas C3b opsonization of acLDL was only modestly reduced by antiC1q (20 μg/ml). The dose response pattern of anti-C1q and its reduction on C3b deposition on LDL is comparable to its control IgM, whereas increasing concentrations of anti-C1q showed a more linear reduction in C3b opsonization of acLDL (A). The addition of d-mannose to 10% NHS reduced C3b deposition on LDL, but not on acLDL. The reduction in C3b opsonization of LDL by d-mannose was similar to its control mannan (B). Binding of LDL to CHO-CR1 was significantly reduced by the addition of d-mannose (100 mm), MgEGTA (20 mm) or EDTA (20 mm) to normal human serum (NHS). Anti-C1q (20 μg/ml) to NHS resulted in a non-significant reduction in LDL binding to CHO-CR1 (C). AcLDL binding to CHO-CR1 was only reduced by the addition of EDTA to NHS, but not by anti-C1q, d-mannose, or MgEGTA (D). Every figure represents the relative mean ± S.E. of at least three experiments. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01.