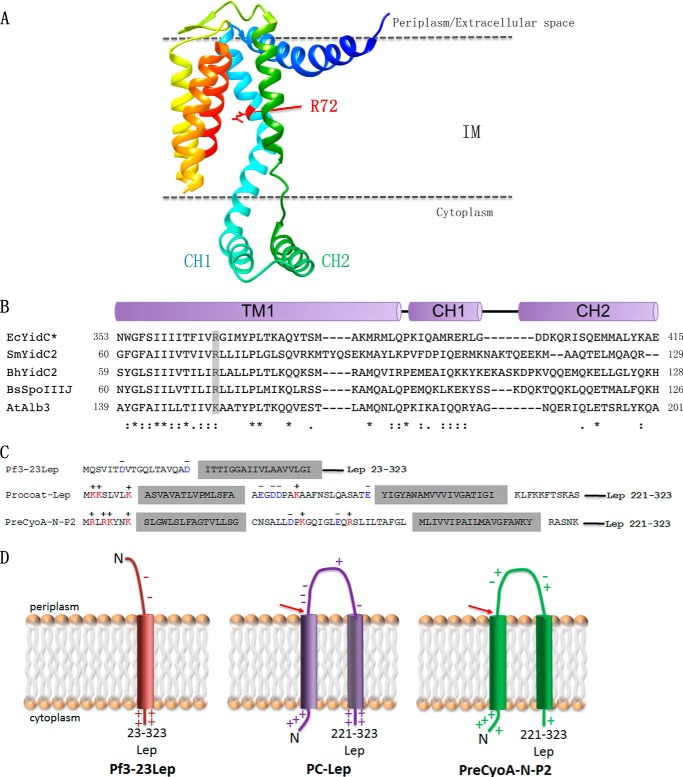
FIGURE 1.
Crystal structure of B. halodurans YidC2 highlighting the conserved positive charge in the hydrophilic groove. A, ribbon representation of the structure of the B. halodurans YidC2. The conserved positively charged Arg-72 (corresponding to Arg-366 in E. coli YidC) is highlighted in red and is located near the top of the hydrophilic groove. B, sequence alignment between YidC homologs in E. coli (Ec), S. mutans (Sm), B. halodurans (Bh), B. subtilis (Bs), and A. thaliana (At). The conserved positively charged residue in TM1 (corresponding to TM2 in the E. coli YidC) that is essential for function of the B. subtilis SpoIIIJ (YidC1) is highlighted in gray. CH1 and CH2 correspond to the N- and C-terminal amino acid sequences that make up the helical hairpin structure. C, YidC substrate constructs used in this study (for details see “Experimental Procedures”), and D, topology of the substrates Pf3-23Lep, PC-Lep, and PreCyoA-N-P2. The red arrows highlight the cleavage site for signal peptidases.