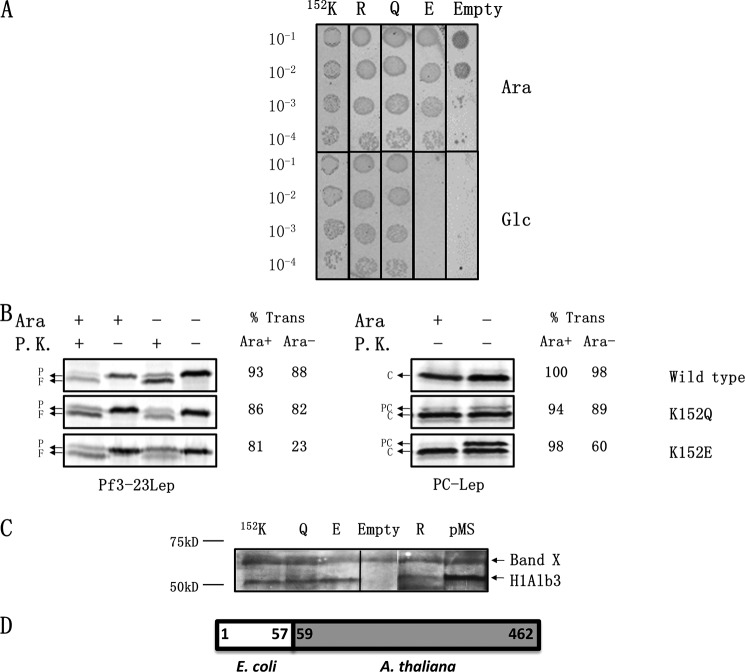
FIGURE 5.
Positively charged residue at 152 in the A. thaliana Alb3 is not critical for function. A, complementation assay to determine the importance of the strictly conserved positively charged residue. The H1Alb3 WT, K152R, K152Q, and K152E mutants were tested for their ability to complement the YidC depletion strain using the spot test, as described in Fig. 2A. H1Alb3 contains the first 57 amino acids of E. coli YidC fused to residues 59–462 of Alb3. B, WT H1Alb3, K152Q and K152E were tested for their ability to insert Pf3-23Lep and PC-Lep using protease mapping (left panel) and signal peptide cleavage (right panel), respectively. The percent translocation of Pf3-23Lep and PC-Lep was quantified as described under “Experimental Procedures.” P represents Pf3-23Lep protein; F denotes the proteinase K fragment; PC represents PC-Lep; C denotes C-Lep protein generated by SP1 cleavage. C, Western blotting to examine expression of the wild-type and H1Alb3 mutants using antibodies generated against a C-terminal peptide from P. sativum Alb3. The top band is an unrelated band seen in our Western blots. The pMS lane refers to H1Alb3 overexpressed in pMS119 to confirm that the band we are examining is indeed H1Alb3. D, schematic of H1Alb3. It contains the first 57 amino acids of E. coli YidC, a linker valine residue, and residues 59–462 of Alb3. P.K., proteinase K.