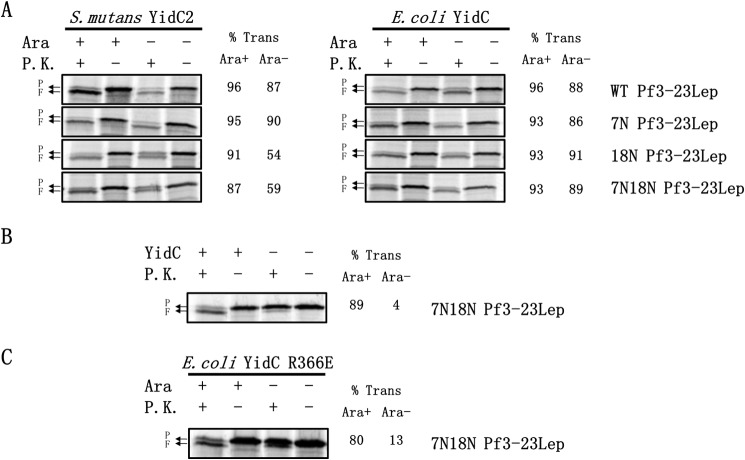
FIGURE 6.
Test of the electrostatic attraction model for how YidC facilitates translocation of the N-tail of Pf3–23Lep across the membrane. The negatively charged residue in the N-tail is important for membrane insertion mediated by S. mutans 247YidC2 but not by the E. coli YidC. A, E. coli YidC (right panel) or S. mutans YidC2 (left panel) was tested for their ability to insert Pf3-23Lep WT, Pf3-23Lep7N, Pf3-23Lep18N, and Pf3-23Lep7N18N. JS7131 bearing pACYC184 encoding E. coli YidC or S. mutans 247YidC2 was transformed with pMS119 encoding Pf3-23Lep proteins. Expression of the Pf3-23Lep mutants, labeling, and membrane insertion was performed as described in Fig. 2B. B, YidC is required for membrane insertion of Pf3-23Lep7N18N. JS7131 expressing YidC or depleted for YidC (−) was analyzed for N-tail translocation. P represents Pf3-23Lep protein; F denotes the proteinase K fragment. C, R366E YidC is defective in translocating the N-tail of Pf3-23Lep lacking negatively charged residues. JS7131 bearing pACYC184 encoding E. coli YidC R366E was transformed with pMS119 encoding Pf3-23Lep7N18N and analyzed for N-tail translocation, as described in Fig. 2B. The percent translocation of Pf3-23Lep and PC-Lep was quantified as described under “Experimental Procedures.” P.K., proteinase K.