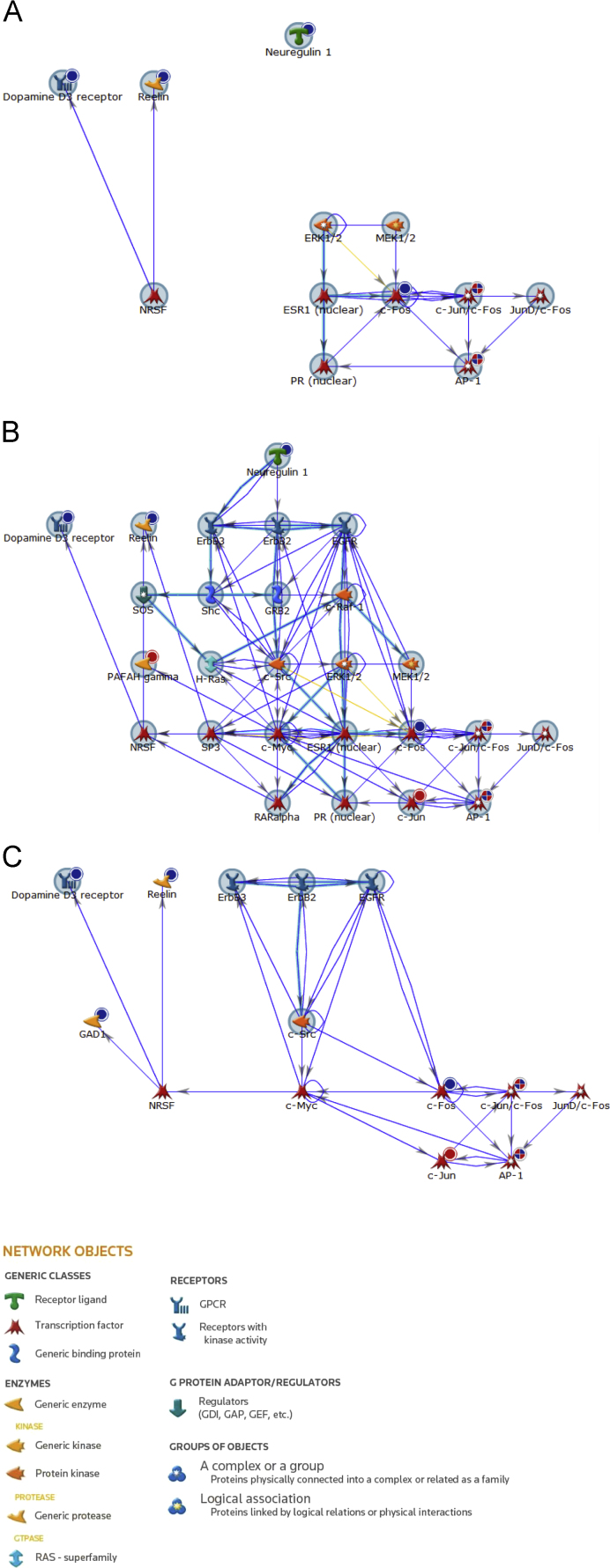
Fig. 2.
Network analysis filters for disease and gene ontology processes. The network generated in relation to genes significantly regulated in response to SH-SY5Y cell treatment with sodium valproate and lithium (Fig. 1) was filtered to show the relevant disease pathways (A and B) and gene ontology processes (C). (A and B) Disease processes relevant to mood disorders (A), represents 46.15% of the gene network; and breast, skin and gastrointestinal neoplasms (B), represents 96.15% of the gene network. (C) Gene ontology processes relevant to drug response. Seed nodes from which the network was built upon are encompassed by a large blue circle. Genes uploaded from the experimental data are also marked with a smaller circle in their top right hand corner; red circles represent genes that were significantly up-regulated, whereas blue circles represent genes significantly down-regulated. Connecting blue arrows indicate direct interactions, yellow arrows indicate interactions that are in the base but do not form part of the network and overlaid cyan lines represent canonical pathways. Gene names/symbols within network A, from top to bottom, left to right: Neuregulin 1, Dopamine D3 receptor, Reelin, ERK1/2, MEK1/2, NRSF, ESR1 (nuclear), c-Fos, c-Jun/c-Fos, JunD/c-Fos, PR (nuclear) and AP-1; B, from top to bottom, left to right: Neuregulin 1, Dopamine D3 receptor, Reelin, ErbB3, ErbB2, EGFR, SOS, Shc, GRB2, c-Raf-1, PAFAH gamma, H-Ras, c-Src, ERK1/2, MEK1/2, NRSF, SP3, c-Myc, ESR1 (nuclear), c-Fos, c-Jun/c-Fos, JunD/c-Fos, RARalpha, PR (nuclear), c-Jun and AP-1; and C, from top to bottom, left to right: Dopamine D3 receptor, Reelin, ErbB3, ErbB2, EGFR, GAD1, c-Src, NRSF, c-Myc, c-Fos, c-Jun/c-Fos, JunD/c-Fos, c-Jun and AP-1. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)