Abstract
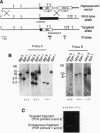
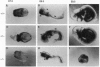
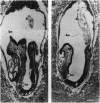
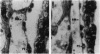
We have targeted the murine thrombomodulin (TM) gene in embryonic stem cells and generated embryos as well as mice with TM deficiency. The heterozygous TM-deficient (TM+/-) mice as compared to wild-type (TM+/+) littermates exhibit 50% reductions in the levels of TM mRNA and TM protein. However, TM+/- mice appear normal and are free of thrombotic complications. The homozygous TM-deficient (TM-/-) embryos die before embryonic day 9.5. An overall retardation in growth and development of TM-/- embryos is first evident on embryonic day 8.5 (8-12 somite pairs). However, no specific pathologic abnormalities are observed. These initial changes take place at a time when TM is normally expressed in the parietal yolk sac. The removal of embryonic day 7.5 TM-/- embryos from maternal decidua and their subsequent culture in vitro allow development to proceed to stages not observed in vivo (13-20 somite pairs) with the appearance of normal blood vessels in the visceral yolk sac and embryo. The results of our studies suggest that the failure of TM-/- embryos to survive at mid-gestation is a consequence of dysfunctional maternal-embryonic interactions caused by the absence of TM in the parietal yolk sac and demonstrate that the receptor is necessary for normal embryonic development in utero.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baldwin H. S., Lloyd T. R., Solursh M. Hyaluronate degradation affects ventricular function of the early postlooped embryonic rat heart in situ. Circ Res. 1994 Feb;74(2):244–252. doi: 10.1161/01.res.74.2.244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertina R. M., Koeleman B. P., Koster T., Rosendaal F. R., Dirven R. J., de Ronde H., van der Velden P. A., Reitsma P. H. Mutation in blood coagulation factor V associated with resistance to activated protein C. Nature. 1994 May 5;369(6475):64–67. doi: 10.1038/369064a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boffa M. C., Burke B., Haudenschild C. C. Preservation of thrombomodulin antigen on vascular and extravascular surfaces. J Histochem Cytochem. 1987 Nov;35(11):1267–1276. doi: 10.1177/35.11.2821107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bovill E. G., Bauer K. A., Dickerman J. D., Callas P., West B. The clinical spectrum of heterozygous protein C deficiency in a large New England kindred. Blood. 1989 Feb 15;73(3):712–717. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmeliet P., Schoonjans L., Kieckens L., Ream B., Degen J., Bronson R., De Vos R., van den Oord J. J., Collen D., Mulligan R. C. Physiological consequences of loss of plasminogen activator gene function in mice. Nature. 1994 Mar 31;368(6470):419–424. doi: 10.1038/368419a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esmon C. T. The regulation of natural anticoagulant pathways. Science. 1987 Mar 13;235(4794):1348–1352. doi: 10.1126/science.3029867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford V. A., Kennel S. J. An intracisternal A-particle DNA sequence is closely linked to the thrombomodulin gene in some strains of laboratory mice. DNA Cell Biol. 1993 May;12(4):311–318. doi: 10.1089/dna.1993.12.311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George E. L., Georges-Labouesse E. N., Patel-King R. S., Rayburn H., Hynes R. O. Defects in mesoderm, neural tube and vascular development in mouse embryos lacking fibronectin. Development. 1993 Dec;119(4):1079–1091. doi: 10.1242/dev.119.4.1079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter E. S., 3rd, Balkan W., Sadler T. W. Improved growth and development of presomite mouse embryos in whole embryo culture. J Exp Zool. 1988 Mar;245(3):264–269. doi: 10.1002/jez.1402450306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imada S., Yamaguchi H., Nagumo M., Katayanagi S., Iwasaki H., Imada M. Identification of fetomodulin, a surface marker protein of fetal development, as thrombomodulin by gene cloning and functional assays. Dev Biol. 1990 Jul;140(1):113–122. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(90)90058-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoué S., Leblond C. P., Laurie G. W. Ultrastructure of Reichert's membrane, a multilayered basement membrane in the parietal wall of the rat yolk sac. J Cell Biol. 1983 Nov;97(5 Pt 1):1524–1537. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.5.1524. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennel S. J., Lankford T., Hughes B., Hotchkiss J. A. Quantitation of a murine lung endothelial cell protein, P112, with a double monoclonal antibody assay. Lab Invest. 1988 Nov;59(5):692–701. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King B. F. The permeability of the guinea pig parietal yolk sac placenta to peroxidase and ferritin. Am J Anat. 1972 Jul;134(3):365–376. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001340307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung C. C. Embryotoxic effects of heterologous antisera against rat Reichert's membrane. J Exp Zool. 1977 May;200(2):295–301. doi: 10.1002/jez.1402000210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miletich J., Sherman L., Broze G., Jr Absence of thrombosis in subjects with heterozygous protein C deficiency. N Engl J Med. 1987 Oct 15;317(16):991–996. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198710153171604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salem H. H., Maruyama I., Ishii H., Majerus P. W. Isolation and characterization of thrombomodulin from human placenta. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 10;259(19):12246–12251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soifer S. J., Peters K. G., O'Keefe J., Coughlin S. R. Disparate temporal expression of the prothrombin and thrombin receptor genes during mouse development. Am J Pathol. 1994 Jan;144(1):60–69. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsiang M., Lentz S. R., Dittman W. A., Wen D., Scarpati E. M., Sadler J. E. Equilibrium binding of thrombin to recombinant human thrombomodulin: effect of hirudin, fibrinogen, factor Va, and peptide analogues. Biochemistry. 1990 Nov 27;29(47):10602–10612. doi: 10.1021/bi00499a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]