FIG 1.
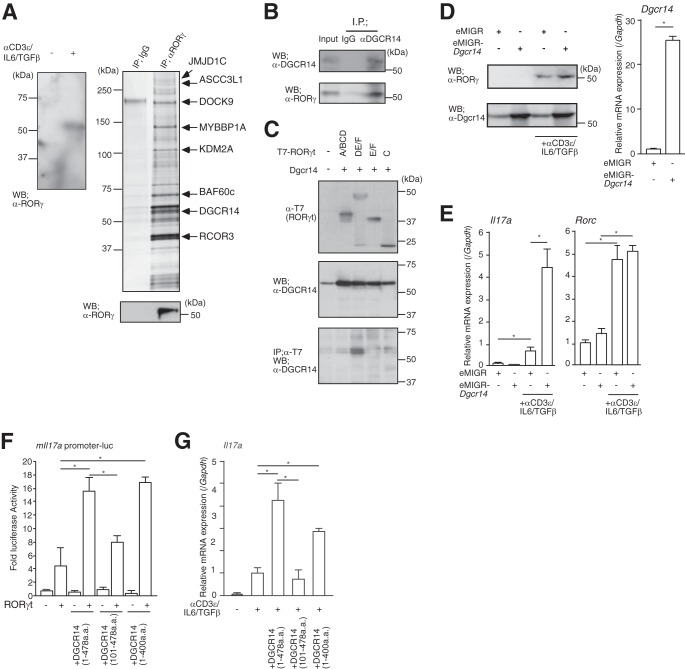
Identification of DGCR14 as a transcriptional coactivator of RORγ. (A) The left panel shows Western blotting for RORγ in 68-41 cells. After stimulation with or without anti-CD3ε antibody, IL-6, and TGF-β, nuclear extracts were prepared and Western blot (WB) assays were performed with the antibodies indicated. The right upper panel shows purification of RORγ-associated proteins from the 68-41 T cell hybridoma line. Large-scale cultures of 68-41 cells were stimulated with anti-CD3ε antibody, IL-6, and TGF-β for 8 h. Nuclear extracts were prepared and purified on anti-RORγ affinity columns and eluted with 0.1 M glycine, pH 3.0. Samples were separated by SDS-PAGE, silver stained, and identified by MALDI-TOF MS analysis (see Table S1 in the supplemental material). Eluted RORγ was detected by Western blotting with anti-RORγ antibody (right lower panel). IP, immunoprecipitation. (B) Immunoprecipitation assays with anti-DGCR14 antibody in 68-41 cells. After stimulation with anti-CD3ε antibody, IL-6, and TGF-β, cells were lysed and precipitated with rabbit IgG or anti-DGCR14 antibody. Western blot assays were performed with the antibodies indicated. (C) Immunoprecipitation assays with T7-tagged RORγt deletion mutant variants (A/BCD, DE/F, E/F, and C). After transfection with each expression vector, 293T cells were lysed and precipitated with anti-T7 antibody (MBL). Western blot assays were performed with the antibodies indicated. (D) The left panels show Western blotting for RORγ and DGCR14 in 68-41 cells with or without Dgcr14 cDNA retroviruses and stimulation with anti-CD3ε antibody, IL-6, and TGF-β. After infection of 68-41 cells with each virus, virus-expressing green fluorescent protein (GFP)-positive cells were sorted with a FACSAria (BD) and cultured. After stimulation with anti-CD3ε antibody, IL-6, and TGF-β, cells were lysed and Western blotting was performed with the antibodies indicated. The right panel shows RT-qPCR analysis for Dgcr14 mRNA in 68-41 cells transduced with Dgcr14 cDNA. Each experiment was performed at least three times, and results are presented as means ± SD. *, P < 0.05. (E) RT-qPCR analyses for Il17a and Rorc mRNAs in 68-41 cells transduced with Dgcr14 cDNA. After stimulation with or without anti-CD3ε antibody, IL-6, and TGF-β, RNA was extracted and RT-qPCR was performed. The mRNA levels of all genes were normalized to the level of Gapdh mRNA expression. Each experiment was performed at least three times, and results are presented as means ± SD. *, P < 0.05. (F) Luciferase reporter assays with Dgcr14 deletion mutant variants and the mIl17a promoter-luciferase reporter vector. After the transduction of each Dgcr14 deletion cDNA expression vector and RORγt expression vector, 68-41 cells were stimulated with anti-CD3ε antibody, IL-6, and TGF-β. The cells were then lysed and used in luciferase reporter assays. As an internal control, o-nitrophenyl-β-d-galactopyranoside (ONPG)-dependent β-gal activities were measured with a microplate reader. Each experiment was performed at least three times, and results are presented as means ± SD. *, P < 0.05. (G) RT-qPCR for assessment of Il17a mRNA in 68-41 cells as described for panel F. The mRNA levels of all genes were normalized to the level of Gapdh mRNA expression. Each experiment was performed at least three times, and results are presented as means ± SD. *, P < 0.05.