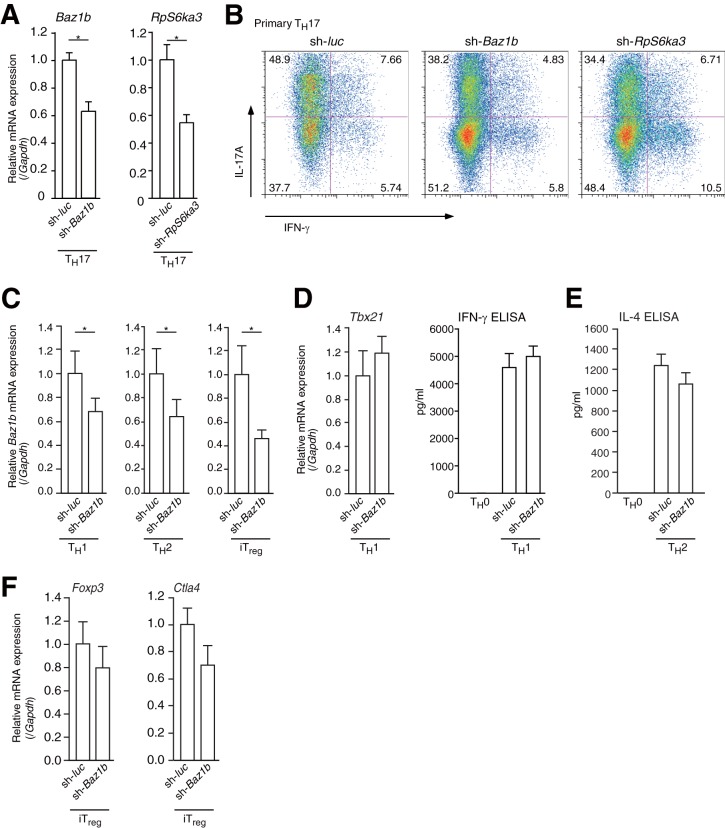
FIG 6.
shRNA for RpS6ka3 or Baz1b reduced TH17 cell differentiation. (A) RT-qPCR analysis of Rps6a3 and Baz1b mRNA expression in primary cultured TH17 cells expressing shRNAs for Rps6a3 (sh-RpS6ka3) or Baz1b (sh-Baz1b). The mRNA levels of all genes were normalized to the level of Gapdh mRNA expression. Each experiment was performed at least three times, and results are presented as means ± SD. *, P < 0.05. (B) Effect of Baz1b or Rps6ka3 shRNA on TH17 differentiation. After transduction with control (sh-luc), Baz1b shRNA (sh-Baz1b), or Rps6ka3 shRNA (sh-Rps6ka3) retrovirus, primary CD4+ T cells were cultured under TH17 conditions (anti-CD3ε, anti-CD28, anti-IFN-γ, and anti-IL-4 antibodies; 10 ng ml−1 IL-6; and 1 ng ml−1 TGF-β) for 4 days. Cells were then analyzed by flow cytometry. (C) RT-qPCR analysis of Baz1b mRNA expression in primary cultured TH1, TH2, and iTreg cells expressing shRNA for Baz1b (sh-Baz1b). mRNA levels of Baz1a were normalized to the level of Gapdh mRNA expression. Each experiment was performed at least three times, and results are presented as means ± SD. *, P < 0.05. (D to F) RT-qPCR analysis of mRNA expression and ELISA for IFN-γ and IL-4 in primary cultured TH1, TH2, and iTreg cells expressing shRNA for Baz1b (sh-Baz1b). The mRNA level of each gene was normalized to the level of Gapdh mRNA expression. Each experiment was performed at least three times, and results are presented as means ± SD. *, P < 0.05.