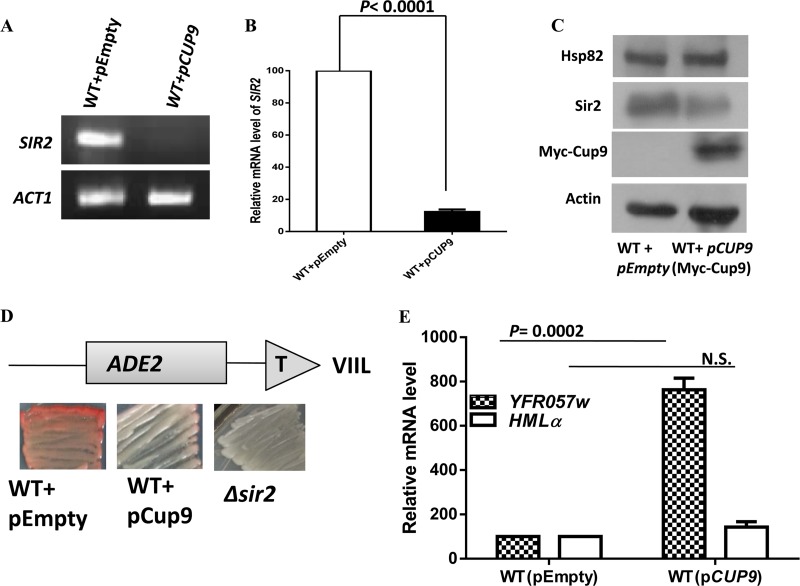
FIG 7.
Cup9 overproduction reduces the endogenous level as well as the function of Sir2. (A) Cup9 was induced by adding galactose to a final concentration of 2%. The overnight culture grown in galactose medium was used as a secondary inoculum in galactose-containing medium and was grown for an additional 5 h (until the mid-log phase) before the isolation of RNA. The effect of Cup9 overexpression on SIR2 transcription was measured by semiquantitative RT-PCR. (B) Real-time RT-PCR quantification of SIR2 mRNA levels in Cup9-overexpressing cells relative to those of the wild-type cells is shown as the average of three experiments. Error bars indicate SD. P values were calculated using the two-tailed Student t test. ACT1 mRNA was used as the normalization control. (C) The overnight culture grown in galactose medium was used for Western blot analysis. The immunoblot shows the reduction of endogenous Sir2 protein upon Cup9 overexpression. The Cup9 overexpression vector harbors C-terminally Myc-tagged Cup9. (D) The ADE2 reporter gene at telomere VIIL was used for the telomere silencing assay. Wild-type, Cup9-overexpressing, and Δsir2 cells were grown and plated as described in Materials and Methods. Pink colonies indicate a silenced ADE2 gene, and white colonies indicate transcriptionally active ADE2. (E) Cup9 overexpression induces the derepression of another subtelomeric gene, YFR057w. However, silencing at the hidden mating type loci is maintained, as seen by the comparable level of the HMLα transcript. ACT1 was used as the normalization control. Error bars indicate SD (n = 3).