Figure 4. Bax/Bak-dependent induction of the IFN response in the absence of active caspases.
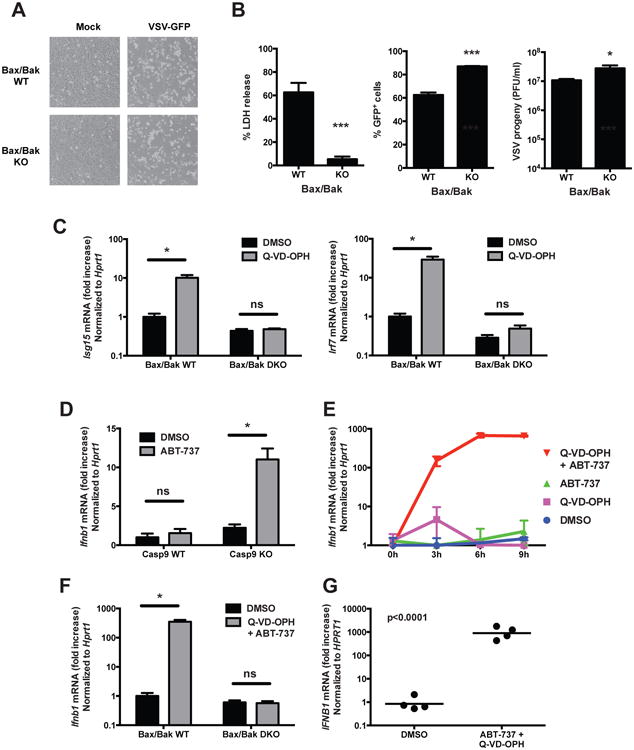
(A and B) Bax/Bak double KO and control immortalized MEFs were infected with VSV-GFP (MOI = 0.5) and their morphology was observed by microscopy (A) and cell death, GFP expression and viral progeny production were determined (B) (mean ± s.d. of triplicates, representative of 3 experiments).
*, p < 0.05; ***, p < 0.001 (two-tailed unpaired t-test).
(C) Bax/Bak WT and double KO MEFs were treated with vehicle (DMSO) or with the caspase inhibitor Q-VD-OPH (10 μM) and the expression of ISGs was measured 48h later by RT-PCR (mean ± s.d. of triplicates, representative of 3 experiments). *, p < 0.05; ns, not significant; pairwise comparisons following two-way ANOVA.
(D) Expression of IFNβ mRNA by Casp9 WT and KO immortalized MEFs after 6h of treatment with vehicle (DMSO) or with the Bcl-2 inhibitor ABT-737 (10 μM) (mean ± s.d. of triplicates, representative of 3 independent experiments).
(E) Expression of IFNβ mRNA by WT primary MEFs at the indicated time points after stimulation with vehicle (DMSO), Bcl-2 inhibitor (ABT-737, 10 μM), caspase inhibitor (Q-VD-OPH, 10 μM) or both inhibitors (mean ± s.d. of duplicates, representative of 3 independent experiments).
(F) Expression of IFNβ mRNA by BaxBak WT and double KO immortalized MEFs after 6h of treatment with vehicle or ABT-737 + Q-VD-OPH (mean ± s.d. of triplicates, representative of 3 independent experiments).
(G) Expression of IFNβ mRNA by human PBMCs after 6h of treatment with vehicle or ABT-737 + Q-VD-OPH (n=4 healthy donors, results combined from 2 independent experiments; p value calculated by two-tailed unpaired Student t-test).
See also Figure S6.
