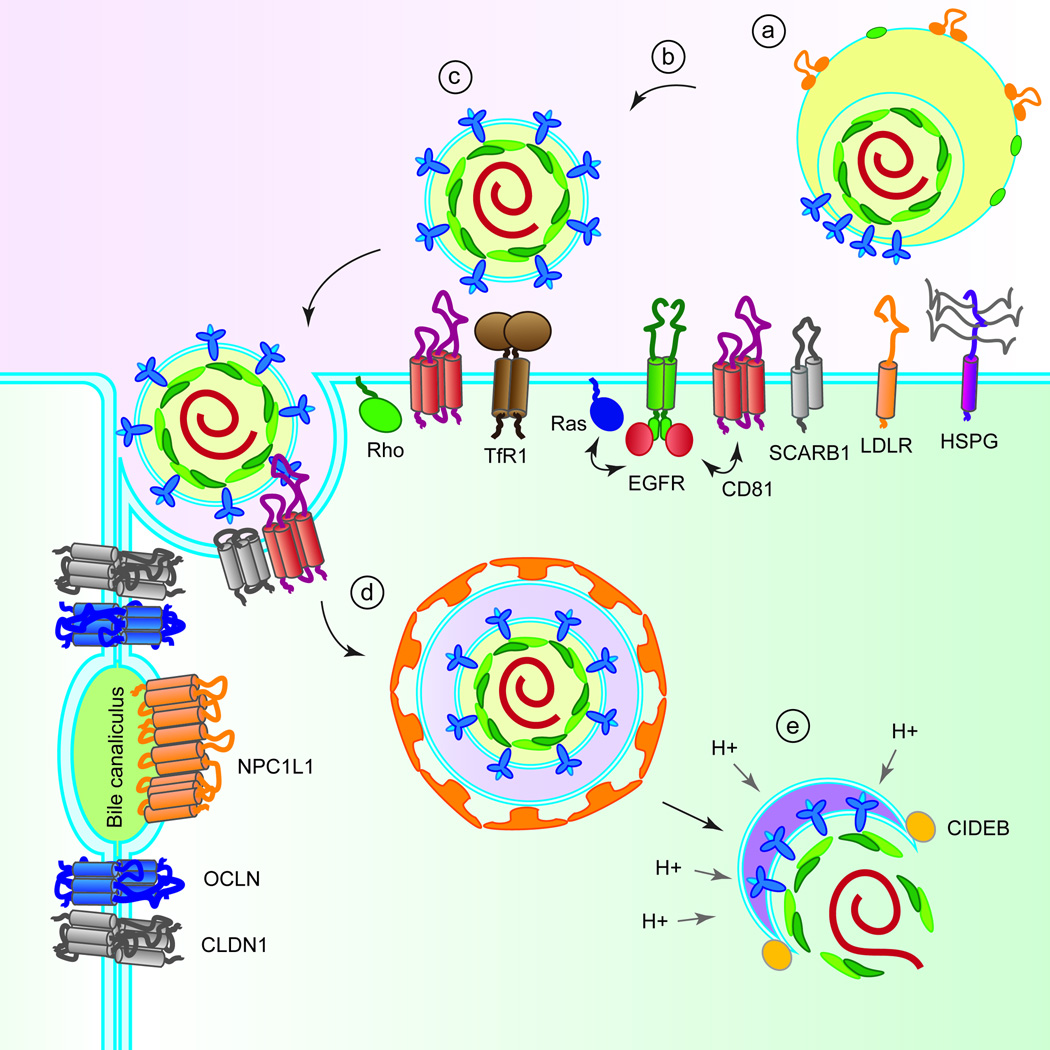
Figure 1.
Putative mechanism of HCV entry. (a) Lipoviral HCV particles attach to HSPG, LDLR and SCARB1. (b) Interaction with SCARB1 induces conformational changes in HCV E2, leading to binding of E2 to CD81. (c) CD81 binding activates signalling pathways via EGFR, Ras and Rho GTPases, triggering lateral membrane diffusion of HCV. The exact roles of TfR1, NPC1L1, CLDN1 and OCLN are not defined but they are engaged in steps post viral attachment and HCV binding to CD81. (d) Interaction of the HCV E2-CD81/CLDN1-complex initiates clathrin-mediated endocytosis. (e) Promoted by an interaction with CIDEB, the viral envelope and the endosomal membrane undergo fusion in a low pH environment.