Abstract
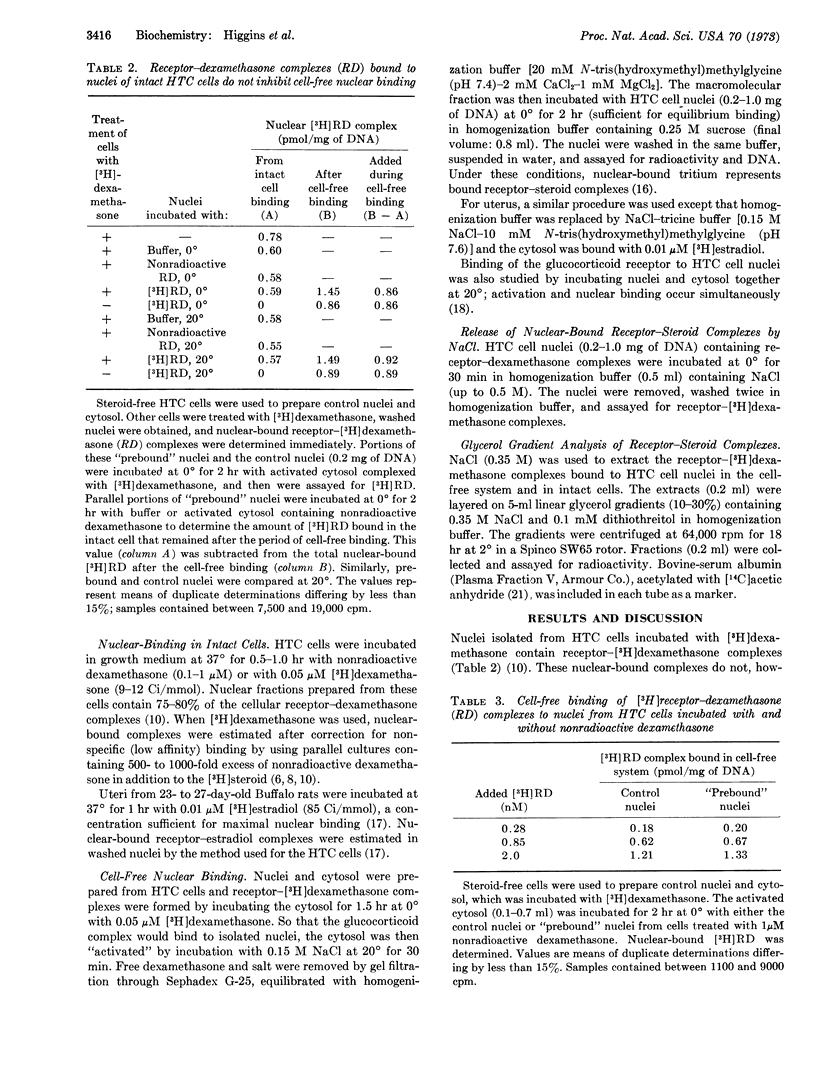
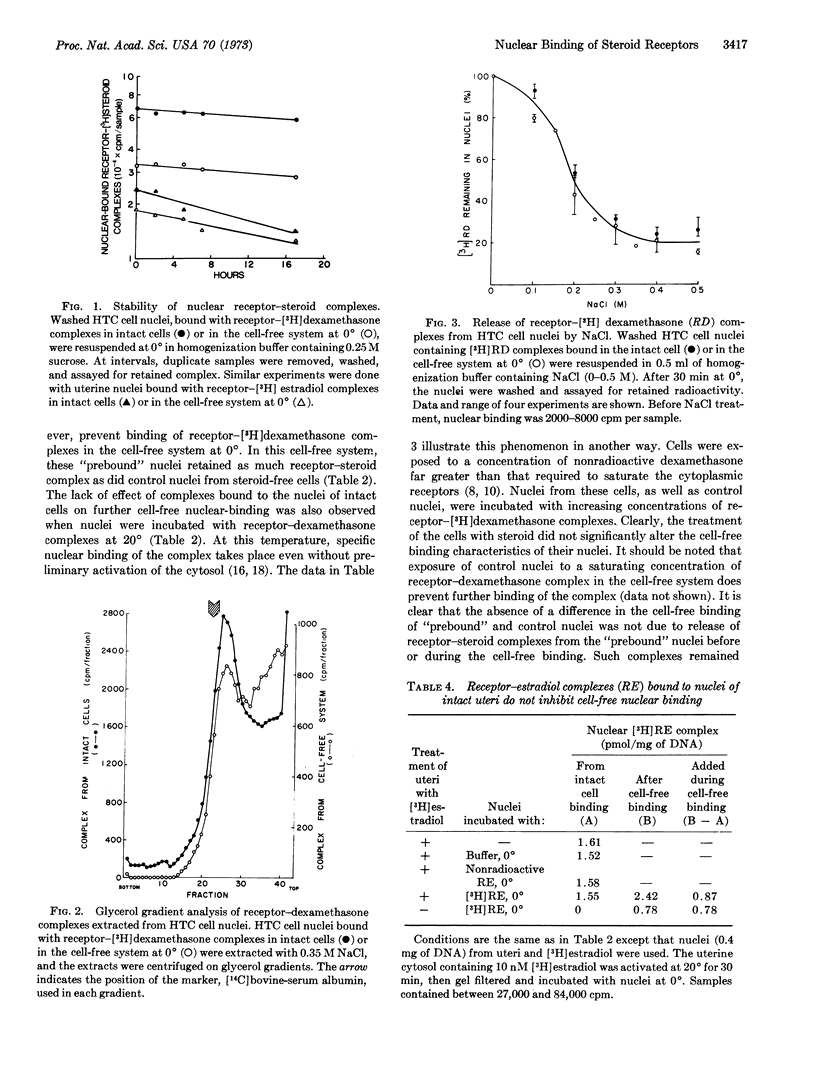
In regulating gene expression in mammalian tissues, steroid hormones bind to cytoplasmic receptors and the resulting complex associates with the nucleus. In an attempt to study this nuclear association under more precisely controlled conditions, we examined the binding of receptor-[3H]steroid complexes to isolated nuclei. Two systems were used: the glucocorticoid-responsive hepatoma cell and the estrogen-sensitive immature rat uterus. Cell-free nuclear binding resembles that observed in the intact cell; it requires the receptor-steroid complex in the appropriate form (“active” complex); it is of high affinity; and it appears to involve about 4000 nuclear acceptor sites per haploid genome. Furthermore, whether binding occurs in intact cells or in cell-free extracts, complexes dissociate from nuclei at similar rates, and the ability of NaCl to extract either type of nuclear-bound complex and the sedimentation velocities of the extracted complexes are identical. Despite these similarities, acceptor sites detected in isolated nuclei differ from those of intact cells, since in neither hepatoma cells nor in the uterus do complexes bound to the nuclei of intact cells prevent further cell-free binding. We conclude that receptor-steroid complexes bind to acceptor sites in isolated nuclei that are chemically similar to, but topographically different from, those of the intact cell.
Keywords: glucocorticoids, estrogens, gene regulation, chromatin
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baxter J. D., Forsham P. H. Tissue effects of glucocorticoids. Am J Med. 1972 Nov;53(5):573–589. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(72)90154-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxter J. D., Rousseau G. G., Benson M. C., Garcea R. L., Ito J., Tomkins G. M. Role of DNA and specific cytoplasmic receptors in glucocorticoid action. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jul;69(7):1892–1896. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.7.1892. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxter J. D., Tomkins G. M. Specific cytoplasmic glucocorticoid hormone receptors in hepatoma tissue culture cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 May;68(5):932–937. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.5.932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxter J. D., Tomkins G. M. The relationship between glucocorticoid binding and tyrosine aminotransferase induction in hepatoma tissue culture cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Mar;65(3):709–715. doi: 10.1073/pnas.65.3.709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R. J., Felsenfeld G. Structure of chromatin. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jan 27;229(4):101–106. doi: 10.1038/newbio229101a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giannopoulos G., Gorski J. Estrogen receptors. Quantitative studies on transfer of estradiol from cytoplasmic to nuclear binding sites. J Biol Chem. 1971 Apr 25;246(8):2524–2529. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins S. J., Rousseau G. G., Baxter J. D., Tomkins G. M. Early events in glucocorticoid action. Activation of the steroid receptor and its subsequent specific nuclear binding studied in a cell-free system. J Biol Chem. 1973 Aug 25;248(16):5866–5872. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins S. J., Rousseau G. G., Baxter J. D., Tomkins G. M. Nature of nuclear acceptor sites for glucocorticoid- and estrogen-receptor complexes. J Biol Chem. 1973 Aug 25;248(16):5873–5879. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen E. V., Numata M., Brecher P. I., Desombre E. R. Hormone-receptor interaction as a guide to biochemical mechanism. Biochem Soc Symp. 1971;32:133–159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen E. V., Suzuki T., Kawashima T., Stumpf W. E., Jungblut P. W., DeSombre E. R. A two-step mechanism for the interaction of estradiol with rat uterus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Feb;59(2):632–638. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.2.632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen R. H., Chalkley R. The physical state of nucleohistone under physiological ionic strength. The effect of interaction with free nucleic acids. Biochemistry. 1968 Dec;7(12):4388–4395. doi: 10.1021/bi00852a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinson B. B., Baxter J. D., Rousseau G. G., Tomkins G. M. Cellular site of glucocorticoid-receptor complex formation. Science. 1972 Jan 14;175(4018):189–190. doi: 10.1126/science.175.4018.189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulrow P. J., Forman B. H. The tissue effects of mineralocorticoids. Am J Med. 1972 Nov;53(5):561–572. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(72)90153-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rousseau G. G., Baxter J. D., Tomkins G. M. Glucocorticoid receptors: relations between steroid binding and biological effects. J Mol Biol. 1972 Jun 14;67(1):99–115. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90389-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuels H. H., Tomkins G. M. Relation of steroid structure to enzyme induction in hepatoma tissue culture cells. J Mol Biol. 1970 Aug 28;52(1):57–74. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90177-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott W. A., Shields R., Tomkins G. M. Mechanism of hormonal induction of tyrosine aminotransferase studied by measurement of the concentration of growing enzyme molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Oct;69(10):2937–2941. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.10.2937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shyamala G., Gorski J. Estrogen receptors in the rat uterus. Studies on the interaction of cytosol and nuclear binding sites. J Biol Chem. 1969 Mar 10;244(5):1097–1103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson E. B., Tomkins G. M., Curran J. F. Induction of tyrosine alpha-ketoglutarate transaminase by steroid hormones in a newly established tissue culture cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Jul;56(1):296–303. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.1.296. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D., Gorski J. Kinetic and equilibrium analysis of estradiol in uterus: a model of binding-site distribution in uterine cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Nov;69(11):3464–3468. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.11.3464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson J. D. Recent studies on the mechanism of action of testosterone. N Engl J Med. 1972 Dec 21;287(25):1284–1291. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197212212872508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


