Figure 5.
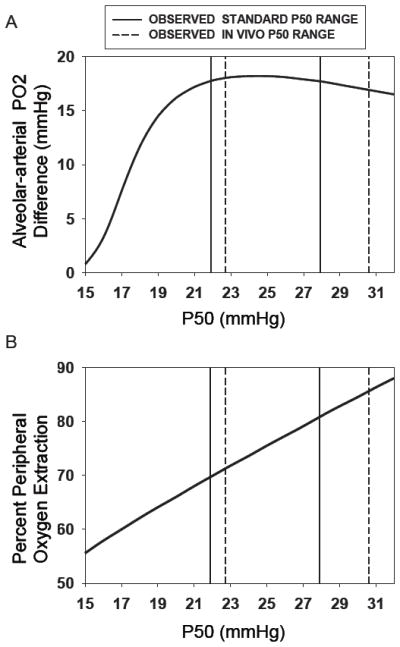
Theoretical calculations of the Alveolar-arterial PO2 difference (AaPO2) (upper panel) and peripheral O2 extraction (lower panel) during peak exercise as a function of standard and in vivo P50 (ranges indicated by solid and dashed lines, respectively). While extraction increases essentially linearly with P50 over a wide range, AaPO2 falls with P50 only when the latter is lower than about 20 mmHg. These outcomes help explain the observations in Figure 4.
