Figure 1.
Rapamycin protects livers from IRI in the presence of inflammation, (a) Serum ALT levels in different groups of mice subjected to either sham operation or 90m ischemia/6h reperfusion treated with vehicle (DMSO) or RPM at 1 or 5mg/kg pre- or post-liver ischemia, as described in the material and methods, (b) Liver histology (H/E stain) and Suzuki scores. Representative tissue sections from either sham-operated or IR livers from DMSO or 1mg/kg RPM treated mice. (c) Quantitative RT-PCR analysis of inflammatory gene expressions in sham-operated and IR livers from DMSO or 1mg/kg RPM treated mice. The ratios of target gene vs. HPRT were plotted against different experimental groups. Note. There were trends of decrease in TNF-α, and CXCL-10 expression levels by RPM, without statistical differences, (d) Serum cytokine levels post liver IR (90m/6h) of different groups of mice. Representative results of at least 2 different experiments. n=3-4/group. *p<0.05, **p<0.01.
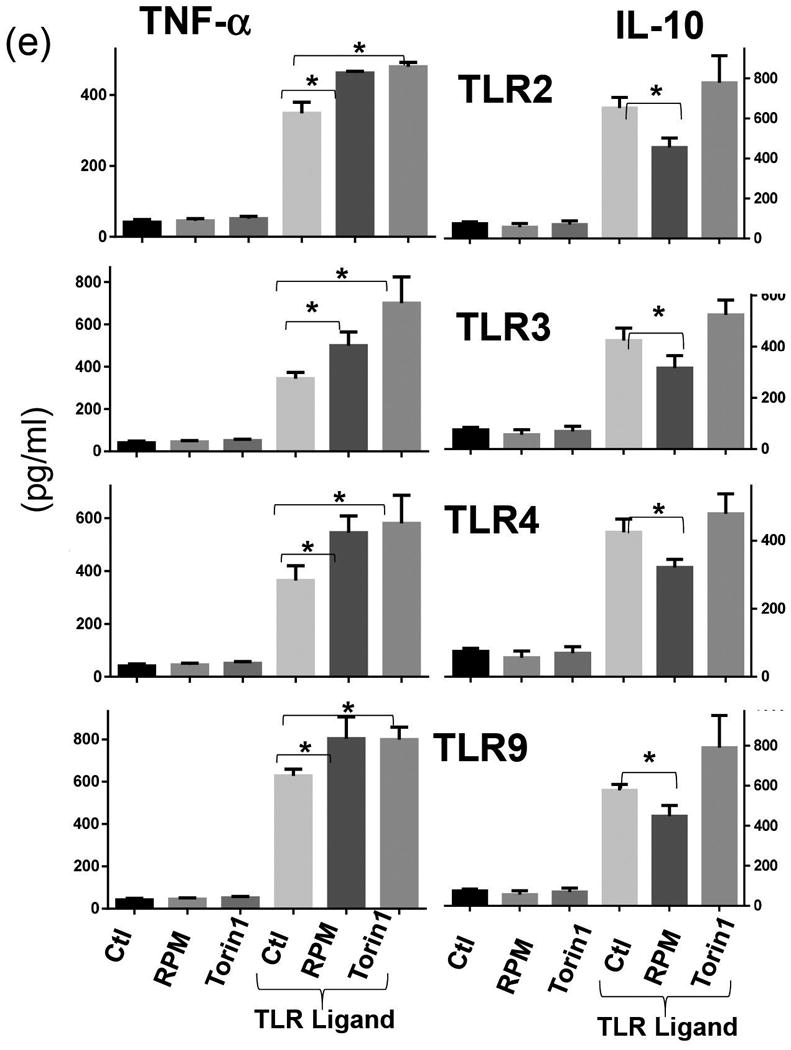
(e) Cytokine productions by Kupffer cells in response to TLR stimulation in vitro. KCs were isolated from B6 mouse livers by in situ collagenase digestion and enriched by selective adherence to petri dishes. After an overnight culture, cells were stimulated with TLR2, or 3, or 4, or 9 ligands for 24hrs in the presence or absence of RPM or Torin 1. TNF-α and IL-10 productions were measured by ELISA.
Representative results of at least 2 different experiments. 3 replicates/group, *p<0.05.
