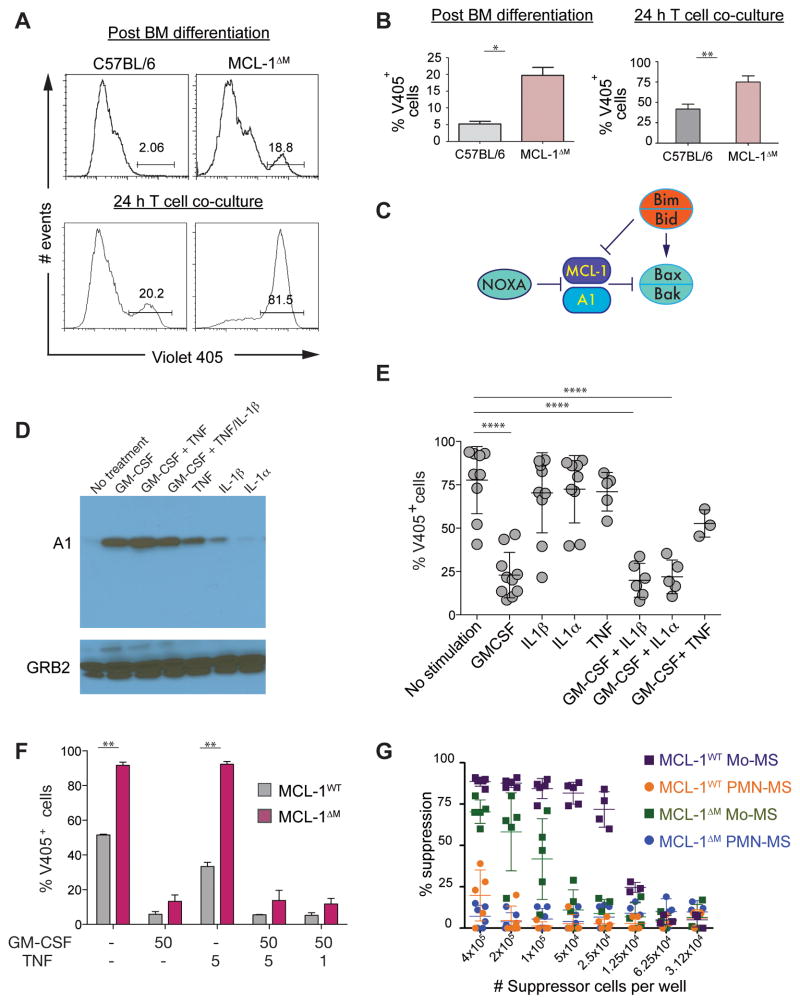
Figure 3. A1 and MCL-1 are needed to maintain the survival of Mo-MS.
(A, B) BM-MS were grown from C57BL/6 or MCL-1ΔM mice. The percentage of cell death was measured by V405 staining of control or MCL-1ΔM Mo-MS at d6 of BM-MS culture (top) or after 24 h T cell suppression assay co-culture (bottom). (B) Quantification of V405+ cells from the experiments representative in (A). Data expressed as the mean ± the s.d. and are representative of two independent experiments. Statistical analysis with unpaired t tests was performed; *p ≤ .05, **p≤ .005. (C) Diagram showing the role of A1 and MCL-1 in inhibiting the mitochondrial death pathway. (D) Lysates from C57BL/6 MS cultures were subjected to immunoblotting for A1 following 24 h stimulation with the cytokines shown, all at 50 ng/mL. GRB2 (~ 26 kDa) was used as the loading control. (E) The percentage of non-viable V405+ Mo-MS after stimulation with cytokines (50 ng/mL). Data expressed as the mean ± s.d. and are representative of no less than 3 independent experiments (n = 2 samples for each experiment). Statistical analysis with unpaired t tests was performed; ****p≤ 0.0001. (F) The percentage of non-viable V405+ Mo-MS was evaluated by V405 staining after 24 h stimulation with the indicated cytokines (ng/mL) (n = 3 independent experiments). Quantification of data, expressed as the mean ± s.d. from one independent experiment. Statistical analysis with unpaired t tests was performed; **p ≤ 0.005. (G) Suppressive function of MS was measured using 5 × 105 CFSE-labeled OT-I cells co-cultured with titrated MS in the presence of SIINFEKL peptide. CFSE dilution was evaluated by flow cytometry after 72 h. Data are compiled from 3 independent experiments, and are presented as mean ± s.d.