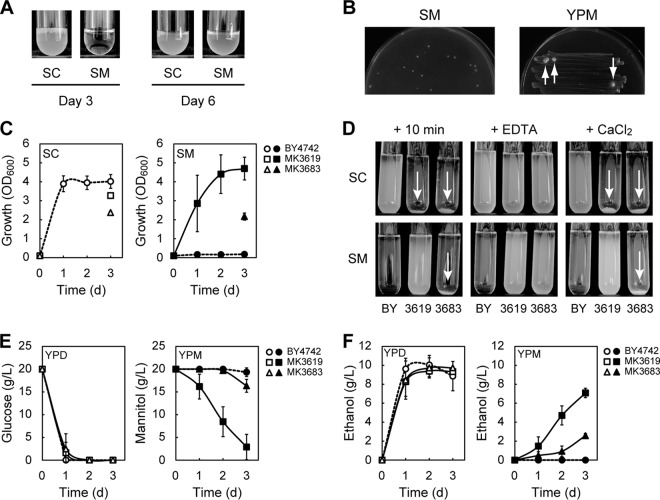
FIG 1.
S. cerevisiae can acquire the ability to assimilate mannitol. (A) BY4742 cells were cultured for 3 or 6 days in SC or SM media, respectively. BY4742 cells that were maintained on YPG plates were inoculated into the medium at an OD600 of 0.10. (B) BY4742 cells that were maintained on YPG plates were grown to log phase in liquid YPD medium and collected. The collected cells (approximately 5 × 106 cells) were spread on SM plates. BY4742 cells grown on YPG plates were also streaked onto YPM plates. SM and YPM plates were incubated for 7 and 16 days, respectively, at 30°C. Visible colonies formed on the YPM plate are indicated by white arrows. (C) Growth of the indicated strains cultured in SC (open symbols) or SM (closed symbols) medium. In the case of flocculated cells, growth was measured only on the third day. (D) Ca2+-dependent flocculation. BY4742 (BY), MK3619, and MK3683 were cultured for 1 day in 5 ml of SC or SM medium, transferred to test tubes, and held for 10 min (+ 10 min). The cultures were mixed with 0.1 volumes of 500 mM EDTA and held for 10 min (+ EDTA). Cells were washed once with water, resuspended in 5 ml of 10 mM CaCl2, and held for 10 min (+ CaCl2). Flocculation is indicated by white arrows. (E and F) Sugar consumption (E) and ethanol production (F) of the indicated cells cultured in YPD (open symbols) or YPM (closed symbols) medium. (C to E) Results are the means of at least three independent experiments, and error bars represent the standard deviations (SDs).