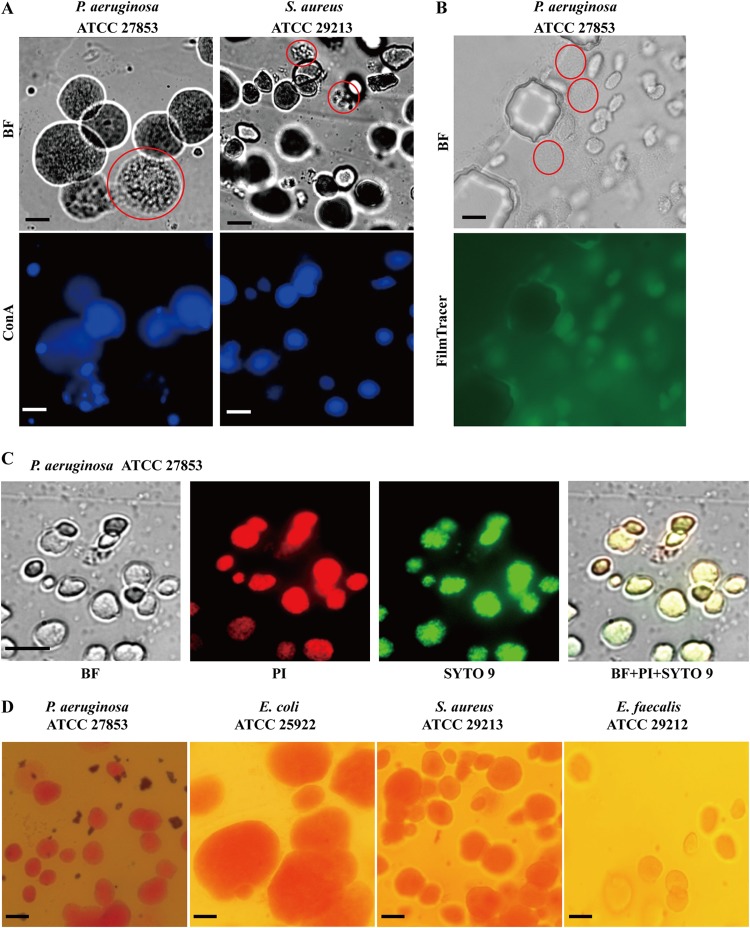
FIG 3.
EPS production in ECASs. (A) ConA staining. The agarose patches containing the ECASs were carefully separated from the MAC chip and directly observed by use of a bright-field (BF) microscope (top row) or stained overnight in ConA solution. After rinsing in PBS, the samples were observed using a fluorescence microscope (bottom row). The bright-field image of P. aeruginosa was also recorded in a movie file, which is provided in Movie S3 in the supplemental material. (B and C) FilmTracer calcein (B) and SYTO 9 and PI (C) staining. The dyes were supplied through a V-shaped channel for 30 min, and ECASs and individual cells were observed with bright-field and fluorescence microscopes. Premature ECASs or simple aggregations of cells, which are poorly stained, are indicated by dotted red circles for comparison with mature ECASs. (D) Congo red staining. The agarose block was removed from the MAC system, stained with a Congo red solution, and observed with a microscope. Microscopes with 40× objective lenses and bright-field (BF), green (FilmTracer and SYTO 9), red (PI), and blue (ConA) filters were used in this study. The exposure time was 400 ms for ConA, 300 ms for SYTO 9 and PI, and 3 s for FilmTracer. Bars, 50 μm.