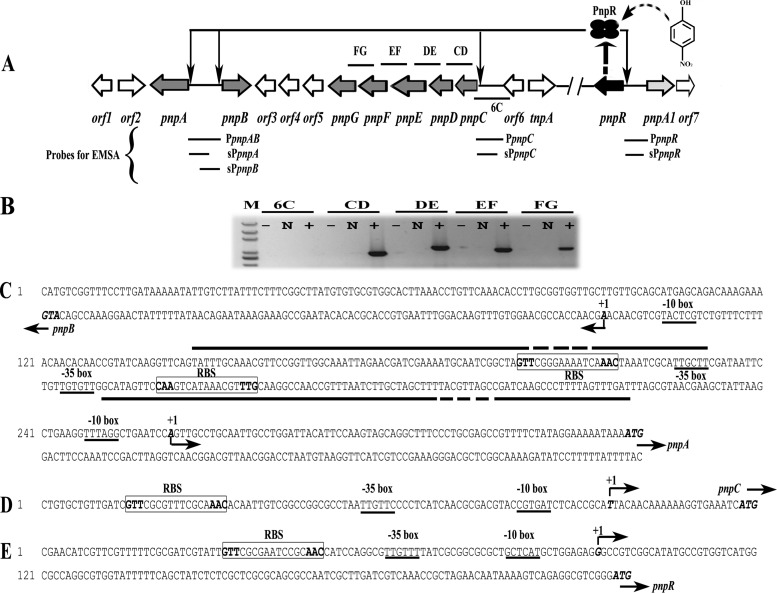
FIG 1.
(A) Schematic of the regulatory circuit of the PNP catabolic cluster in Pseudomonas sp. strain WBC-3 (figure not drawn to scale). Four ellipses represent the PnpR tetramer. The curved and dotted arrow stands for binding of para-nitrophenol (PNP) with PnpR. Four thin arrows represent PnpR's activation of the four pnpA, pnpB, pnpCDEFG, and pnpR operons. Two forward slashes represent a gap in genome. The lengths of probes PpnpAB, sPpnpA, sPpnpB, PpnpC, sPpnpC, PpnpR, and sPpnpR, used in electrophoretic mobility shift assays (EMSAs), were 334 bp, 182 bp, 185 bp, 270 bp, 119 bp, 344 bp, and 217 bp, respectively. The locations of DNA fragments amplified by RT-PCR are represented by short solid lines above (or below) the relevant genes and designated 6C, CD, DE, EF, and FG. (B) Transcriptional organization of the pnpC, pnpD, pnpE, pnpF, and pnpG genes. Strain WBC-3 was grown at 30°C, and mRNA was extracted after PNP induction. The cDNA was synthesized with random primers. Lane M, molecular marker (100-bp ladder; Transgen). +, presence of RT-PCR products; N, the corresponding negative controls with DNase-treated RNA samples; −, the corresponding negative controls with water. The organization of the upstream regions of the four operons of pnpA and pnpB (C), pnpCDEFG (D), and pnpR (E) is shown. The putative −10 boxes and −35 boxes are underlined. The start codon ATG and TSSs are in italic and bold. TSSs are denoted by bent arrows and +1, and the direction of the arrows indicates the direction of gene transcription. The putative regulatory GTT-N11-AAC binding sites (RBSs) are boxed, and the palindrome is in bold. The solid straight lines indicate the PNP binding sites in DNase I footprinting analysis with or without PNP while the fractured portions denote the region where PnpR is bound tighter in the presence of PNP than in the absence of PNP.