Abstract
As in the case with prokaryotic systems, Artemia salina elongation factors EF-1 and EF-2 interact with a common site or with closely overlapping sites on the Artemia ribosome. This feature of ribosomal design must restrict interaction with the ribosome to only one of the factors at alternating steps of chain elongation. In support of this view we find that EF-1, but not EF-2, interacts with the post-translocation ribosome, whereas the reverse is true of the pre-translocation ribosome. Conformational changes probably account for the alternating selectivity of the translating ribosome for each elongation factor.
Keywords: polypeptide chain elongation, eukaryotic ribosomes, Artemia salina
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cabrer B., Vázquez D., Modolell J. Inhibition by elongation factor EF G of aminoacyl-tRNA binding to ribosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Mar;69(3):733–736. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.3.733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caskey T., Leder P., Moldave K., Schlessinger D. Translation: its mechanism and control. Science. 1972 Apr 14;176(4031):195–197. doi: 10.1126/science.176.4031.195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins J. F., Raeburn S., Maxwell E. S. Aminoacyltransferase II from rat liver. II. Some physical and chemical properties of the purified enzyme and its adenosine diphosphate ribose derivative. J Biol Chem. 1971 Feb 25;246(4):1049–1054. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haenni A. L., Chapeville F. The behaviour of acetylphenylalanyl soluble ribonucleic acid in polyphenylalanine synthesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Jan 18;114(1):135–148. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(66)90261-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin S. Y., McKeehan W. L., Culp W., Hardesty B. Partial characterization of the enzymatic properties of the aminoacyl transfer ribonucleic acid binding enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4340–4350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucas-Lenard J. Protein biosynthesis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1971;40:409–448. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.40.070171.002205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCroskey R. P., Zasloff M., Ochoa S. Polypeptide chain initiation and stepwise elongation with Artemia ribosomes and factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Sep;69(9):2451–2455. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.9.2451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKeehan W. L., Hardesty B. Purification and partial characterization of the aminoacyl transfer ribonucleic acid binding enzyme from rabbit reticulocytes. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4330–4339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller D. L. Elongation factors EF Tu and EF G interact at related sites on ribosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Mar;69(3):752–755. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.3.752. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NIRENBERG M., LEDER P. RNA CODEWORDS AND PROTEIN SYNTHESIS. THE EFFECT OF TRINUCLEOTIDES UPON THE BINDING OF SRNA TO RIBOSOMES. Science. 1964 Sep 25;145(3639):1399–1407. doi: 10.1126/science.145.3639.1399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richman N., Bodley J. W. Ribosomes cannot interact simultaneously with elongation factors EF Tu and EF G. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Mar;69(3):686–689. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.3.686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
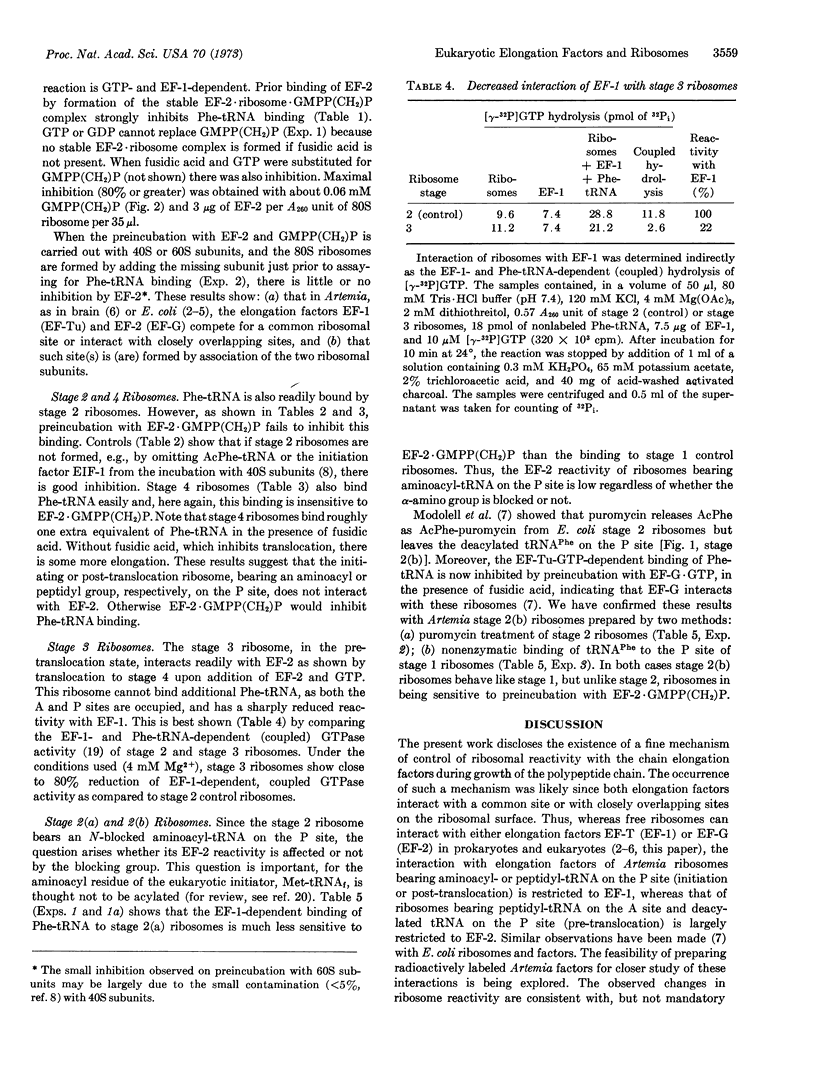
- Richter D. Competition between the elongation factors 1 and 2, and phenylalanyl transfer ribonucleic acid for the ribosomal binding sites in a polypeptide-synthesizing system from brain. J Biol Chem. 1973 Apr 25;248(8):2853–2857. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richter D. Inability of E. coli ribosomes to interact simultaneously with the bacterial elongation factors EF Tu and EF G. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Mar 10;46(5):1850–1856. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90061-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissbach H., Redfield B., Moon H. M. Further studies on the interactions of elongation factor 1 from animal tissues. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1973 May;156(1):267–275. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(73)90365-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zasloff M. Non-enzymic binding of formylmethionyl-transfer RNAf to Artemia salina ribosomes. J Mol Biol. 1973 Jun 5;76(4):445–453. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90483-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zasloff M., Ochoa S. A supernatant factor involved in initiation complex formation with eukaryotic ribosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Dec;68(12):3059–3063. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.12.3059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zasloff M., Ochoa S. Polypeptide chain initiation in eukaryotes. IV. Purification and properties of supernatant initiation factor from Artemia salina embryos. J Mol Biol. 1973 Jan;73(1):65–76. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90159-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


