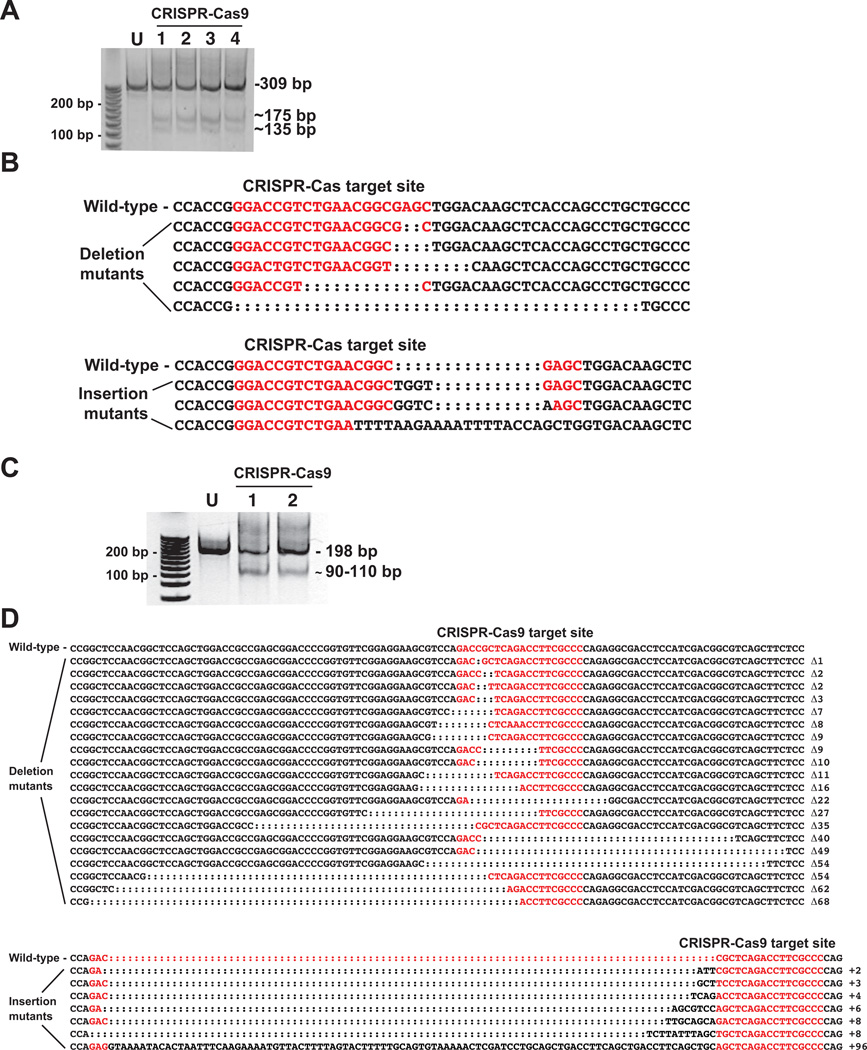
Figure 5.
CRISPR-Cas9-mediated mutagenesis of killifish AHR2b targeting exon 2 and exon 3. A. Surveyor nuclease detection of mutations in the AHR2b CRISPR-Cas9 target region. Each lane represents a pool of 5 embryos from which a 309 bp genomic DNA fragment was amplified. U: uninjected control, lanes 1–4: CRISPR-Cas9-injected embryos. Approximate sizes of the digested fragments containing the deletions and insertions are shown (175 and 135 bp). The full-length PCR products from samples 1–4 were pooled, cloned, and sequenced. B. AHR2b exon 2 sequence surrounding the CRISPR-Cas9 target site (in red). Five types of deletion mutants and 3 types of insertions were observed among the sequenced clones. C. Surveyor nuclease detection of mutations in the CRISPR-Cas9 target region of AHR2b exon 3. Each lane represents a pool of 5 embryos from which a 198 bp genomic DNA fragment was amplified. U: uninjected, lanes 1 and 2: CRISPR-Cas9-injected embryos. Approximate sizes of the digested fragments containing the deletions and insertions are shown (110 and 90 bp). The full-length PCR products from samples 1 and 2 were pooled, cloned, and sequenced. D. AHR2b exon 3 sequence surrounding the CRISPR-Cas9 target site (in red). Twenty different types of deletion mutants and seven types of insertion mutants were observed among the sequenced clones.