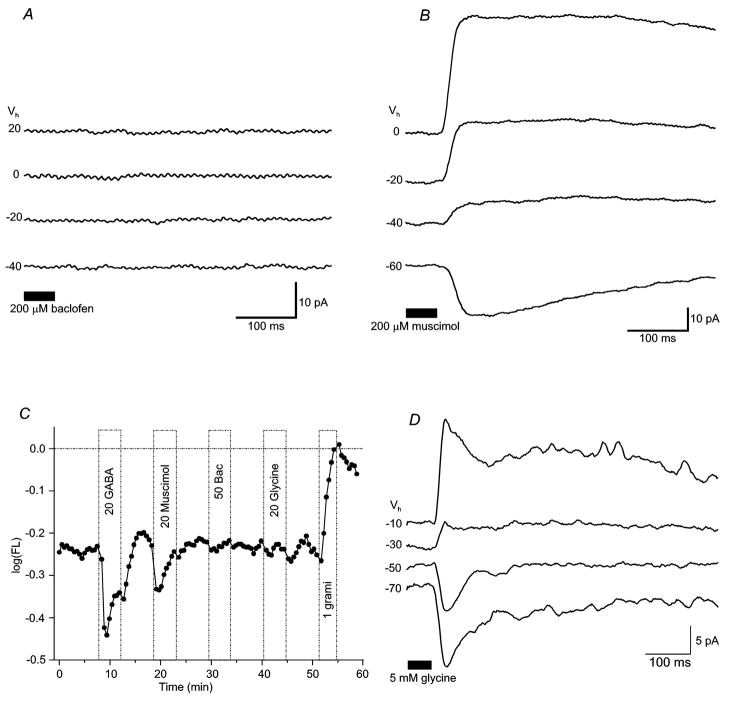
Figure 5. Muscimol, not baclofen, is an effective agonist of GABA receptors on bipolar cell axon terminals.
Whole-cell current traces show responses to (A) 200μM ± baclofen or (B) 200μM muscimol applied onto axon terminals. Erev of muscimol-elicited currents averaged −45.4 ± 21.6mV (n = 4). Baclofen failed to elicit responses. Each drug was tested in separate experiments. (C) Voltage-probe records from a dissociated bipolar cell reveal both GABA- (“20 GABA”) and muscimol-(“20 Muscimol”) induced hyperpolarizations. Baclofen (“50 Bac”) and glycine (“20 gly”) were not effective in this cell, though glycine induced hyperpolarizations in others. (D) Whole-cell current traces show responses to 5 mM glycine applied onto bipolar cell dendrites. Erev of dendritic glycine-elicited currents averaged − 49 ± 9mV (n = 8). Bipolar cells were also sensitive to glycine applied to axonal boutons (not shown). Figure conventions for voltage-probe records are the same as described in Figure 2.