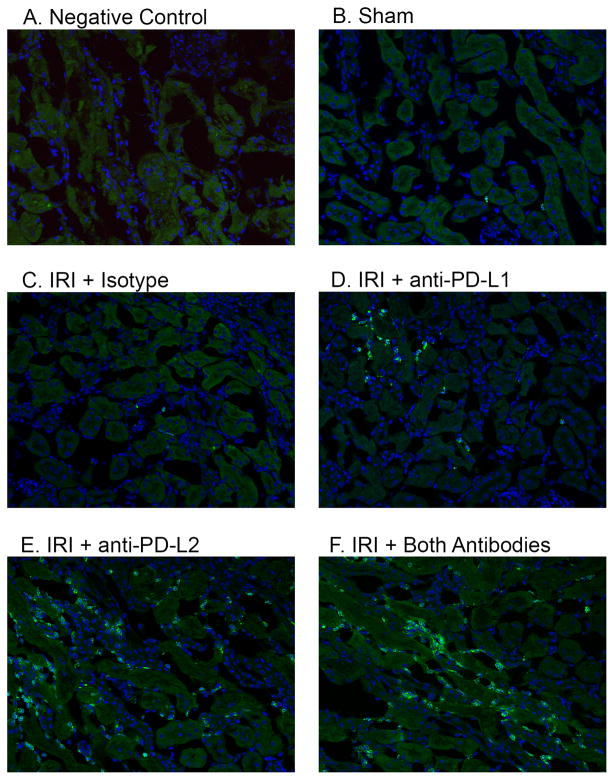
Figure 4. Blocking PD-1 ligands increases innate inflammation in the renal outer medulla after kidney IRI.
Naïve WT mice were treated with isotype control antibodies, anti-PD-L1 or anti-PD-L2 antibodies or the combination of both blocking antibodies. After 24 hours, sham or mild bilateral kidney IR surgery (24 min ischemia) was performed. Frozen kidney sections were stained with DAPI and 7/4 antibodies to detect innate leukocytes. Negative control (A) shows background green autofluorescence in an injured and inflamed mouse kidney. Pictures taken of the outer medulla region of each kidney under 200X magnification are representative of at least 5 mice per treatment group.