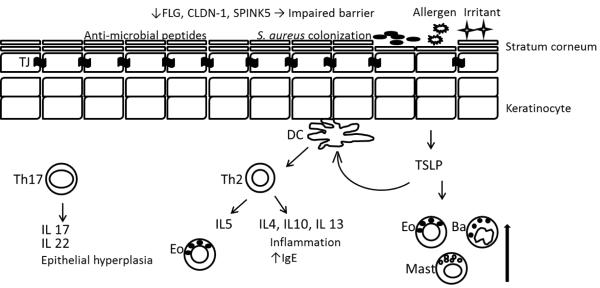
Figure 1.
Defective epidermal barrier in the pathogenesis of AD. A reduction in FLG, CLDN-1, SPINK5, and other injuries lead to increase permeation of allergen and increase trans-epidermal water loss. Decreased antimicrobial peptides, like beta-defensins and cathelicidins result in bacterial colonization. Activated DCs by TSLP from keratinocytes and by antigens stimulate proliferation of Th2 cells. Th2 cells secrete inflammatory cytokines that worsen AD severity. Mast cells, basophils, and eosinophils are induced by TSLP. Th17 cells secrete IL17 and IL22 that can cause epithelial hyperplasia. FLG: filaggrin, CLDN-1: claudin 1, SPINK5: Kazal-type serine protease inhibitor, TJ: tight junction, DC: dendritic cell, TSLP: Thymic stromal lymphopoietin, Eo: eosinophil, Ba: basophil, Mast: mast cell.