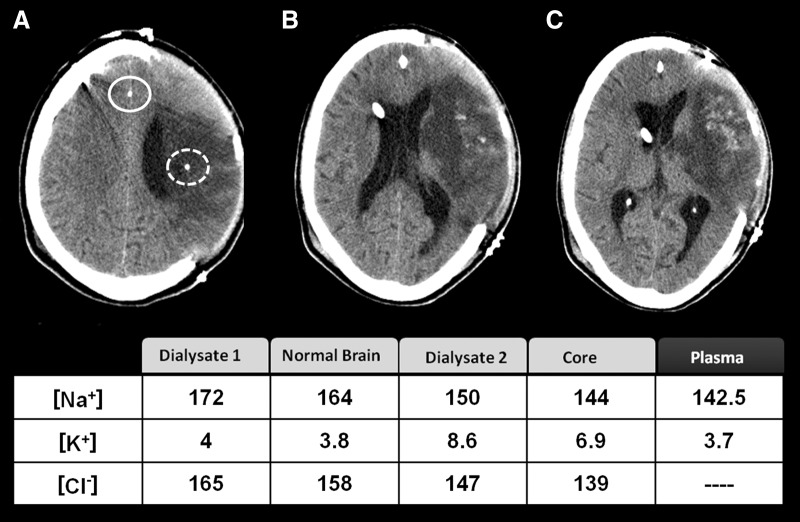
FIG. 6.
This 52-year-old man was brought to the emergency department following the sudden onset of severe right-sided weakness and difficulty speaking. On admission to our center, the patient showed dense right hemiplegia and expression dysphasia and a score on the National Institutes of Health stroke scale of 22. In the computed tomography scan after decompressive craniectomy was conducted, we observed a massive infarction occupying more than 75% of the territory of the middle cerebral artery with some hemorrhagic component inside the infarction. The continuous and discontinuous white circles indicate the MD probes located in normal brain and in the infarction core, respectively. The table summarizes the ionic concentration in the plasma, the dialysate in normal brain (dialysate 1) and core (dialysate 2), and the estimated concentration in the extracellular fluid according to the equations described in the text. The main finding was that [K+]brain was high in the core.