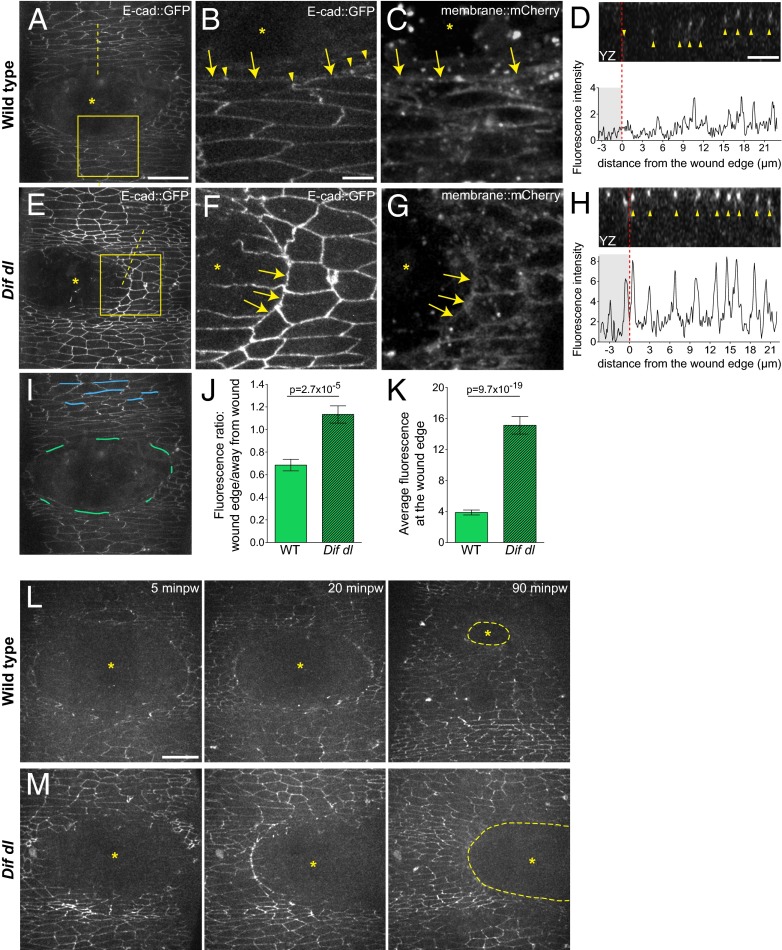
Fig. 3.
Remodeling of E-cad::GFP at the wound edge fails in Dif dl mutants. (A–H) Ventral epidermis of embryos at stage 15 expressing E-cad::GFP and membrane::mCherry. A, B, D–F, and H show E-cad::GFP, whereas C and G show membrane::mCherry. Images are taken with identical settings at 5 min after wounding of wild type (A–D) and Dif dl (E–H). (B, C, F, and G) are high-magnification images of the wound edge in wild-type and Dif dl embryos (boxed regions in A and E). In wild type, wound-edge membranes have low levels of E-cad::GFP (A; B, arrows) compared with cellular junctions at a distance from the wound. In wound-edge cells, E-cad::GFP is present as apical puncta (B, arrowheads) at contact points between the cells. In Dif dl, all epidermal cells, at the wound edge and far from the wound, have high levels of E-cadherin (E; F, arrows). Wound-edge membranes are outlined by membrane::mCherry (C and G). Asterisks mark the wound. (D and H) YZ cross sections of the epidermis (apical side is up). Dashed lines in A and E mark the positions of the cross-sections. The graphs show the fluorescence intensity profiles of E-cad::GFP in these YZ cross-sections. The wound area is shaded; the wound margin is marked with a red dashed line. Both wild-type and Dif dl embryos display apical localization of E-cad::GFP (arrowheads in D and H). Wild-type cells have low levels of E-cad::GFP at the wound edge, whereas Dif dl cells retain high levels of fluorescence. (I) Schematic representation of the wound-edge membranes (green lines) and AJs (blue lines) used for the measurements and quantification of E-cad::GFP fluorescence shown in J and K. (J) Ratio of E-cad::GFP at wound-edge membranes versus E-cad::GFP at AJs away from the wound in wild type and in Dif dl. In wild type, this ratio is significantly lower (0.685 ± 0.050) than in Dif dl (1.133 ± 0.076), P = 2.7 x 10−5 (Mann–Whitney test). Error bars are SEM. (K) E-cad::GFP fluorescence intensity at the membranes surrounding the wound in wild type and in Dif dl. Compared with wild type, Dif dl embryos show significantly higher E-cad::GFP fluorescence (P = 9.7 × 10−19, Mann–Whitney test). The value in Dif dl (15.13 ± 1.136) is nearly fourfold higher than in wild type (3.872 ± 0.318). Measurements of 92 wound-edge membranes from 6 wild-type embryos and 91 wound-edge membranes from 5 Dif dl embryos are plotted. Error bars represent SEM. (L) Wound closure dynamics in wild-type embryo expressing E-cad::GFP. Images are single time points from Movie S1. The initial wound of 2,795 μm2 closes rapidly and at 90 min after wounding (minpw), the remaining gap (outlined with a dashed line) is 15-fold smaller: 198.3 μm2. (M) Wound closure dynamics in Dif dl embryo expressing E-cad::GFP. Images are single time points from Movie S3. The initial wound of 2,750 μm2 remains open and at 90 min minpw is approximately 2,157.5 μm2, which is only a 1.3-fold reduction in gap size. (Scale bars: A, E, I, L, and M, 20 μm; B–D and F–H, 5 μm.)