Fig. 2.
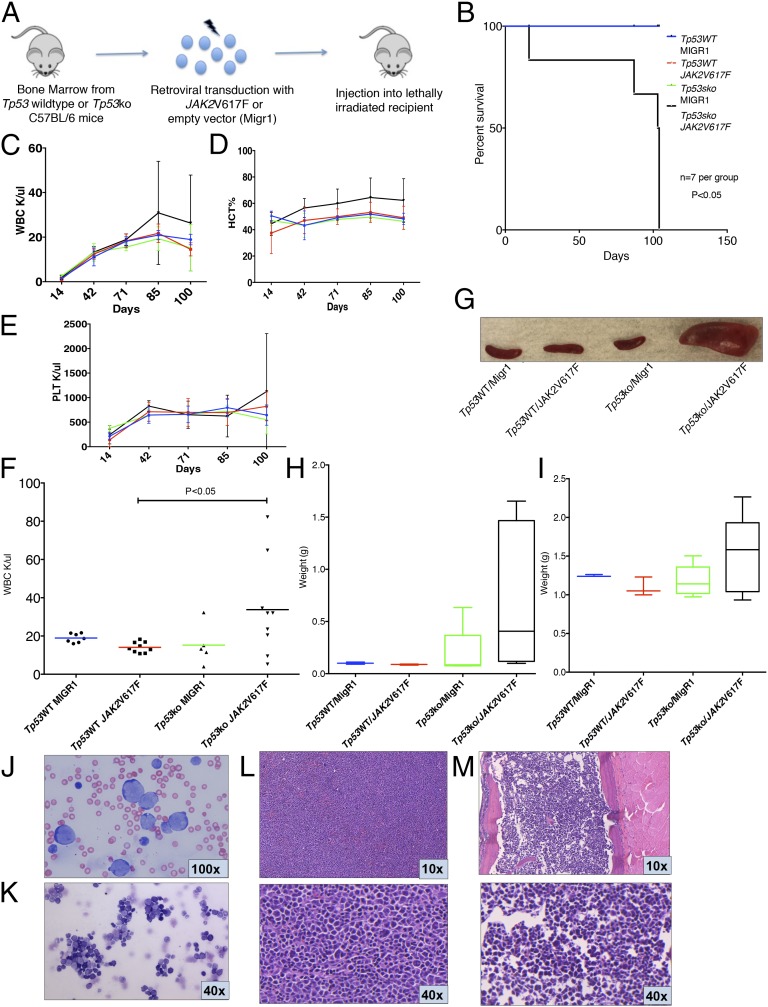
JAK2V617F collaborates with Tp53 loss to induce AML. (A) Bone marrow from Tp53-null (Tp53-KO) or wild-type C57BL/6 mice was harvested and transduced with either JAK2V617F- or MigR1-containing retrovirus. Transduced cells then were injected into lethally irradiated congenic recipients. (B) Survival of mice injected with Tp53-KO bone marrow transduced with JAK2V617F (Tp53-KO/JAK2V617F) was reduced significantly compared with control arms (P < 0.01, t test). (C–E) Trend of WBC (C), HCT (D), and PLT (E) in Tp53-KO/JAK2V617F mice compared with control arms from day 14 posttransplantation to day 100. (F) WBC count of recipients injected with Tp53-KO/JAK2V617F bone marrow was significantly greater than that of p53WT/JAK2V617F control (P < 0.05, t test) at day 100 posttransplantation, with a trend toward increase compared with other control arms. Blood counts displayed are derived from two independent experiments. (G) Representative spleens from killed animals. (H and I) Spleen (H) and liver (I) weights demonstrating increased organ weights in Tp53WT/JAK2V617F mice. (J and K) Representative peripheral blood smear (J) and bone marrow cytospin (K) from Tp53WT/JAK2V617F mice demonstrate increased numbers of intermediate to large blasts with round and irregular nuclei, high nuclear:cytoplasmic ratios, and finely stippled chromatin, consistent with acute leukemia; maturing myeloid and erythroid precursors are markedly reduced (Wright–Giemsa stain). (L and M) Representative spleen sections (L) and bone marrow (M) from Tp53WT/JAK2V617F mice demonstrating increased blasts consistent with acute leukemia (H&E stain).