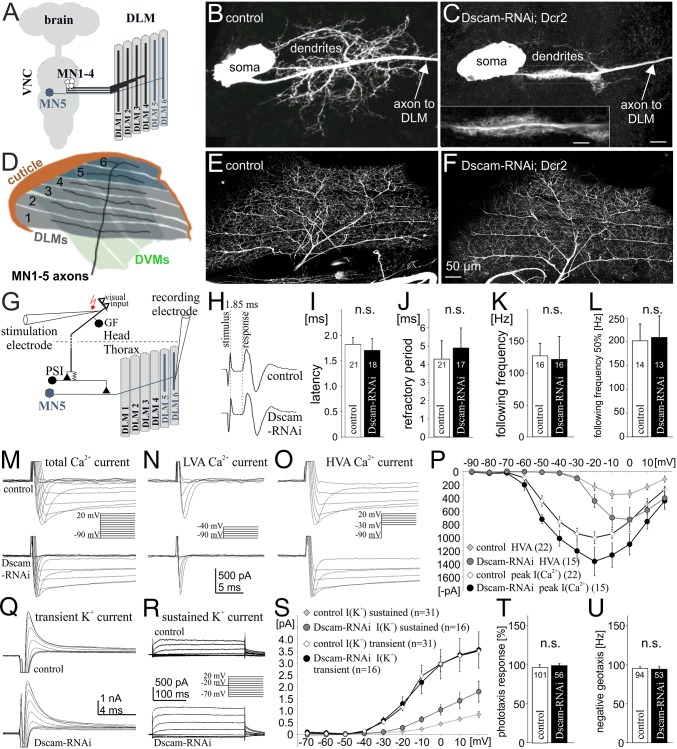
Fig. 1.
Selective manipulation of dendrites. (A) Schematic of Drosophila dorsal longitudinal wing depressor muscle and its innervation by motoneurons, MN1–5. (B) Representative image of MN5 dendritic structure in a control. (C) MN5 structure after targeted RNAi knockdown of Dscam1. (D) Schematic of DLM fibers with MN1–5 axon arbors. (E and F) MN1–5 axonal projections and collateral branches are similar in controls (E) and after dendrite elimination (F). (G) Schematic of the Drosophila neuronal escape circuit. Visual input is relayed to the GF interneuron that makes a mixed electrical chemical synapse onto the PSI, which in turn bypasses all dendrites and synapses onto the axons of MN1–5. (H) Postsynaptic responses in the DLM muscle after GF stimulation are identical in controls and after genetic elimination of most motoneuron dendrites, indicating normal speed of action potential propagation and synaptic transmission. (I–L) Reliability of synaptic transmission is not affected by dendritic defects. Refractory period remains unaltered (J); the pathway follows stimulation frequencies of approximately 130 Hz with 100% reliability (K) and up to 200 Hz with 50% reliability (L). (M) MN5 voltage-gated Ca2+ currents are qualitatively similar in controls and with 90% dendrite reduction, both with respect to low-voltage activated (LVA) (N) and high-voltage activated (HVA) currents (O). (P) Activation voltages of LVA and HVA currents are identical in controls (n = 22) and manipulated neurons (n =15), but current amplitudes as recorded from the soma are larger in neurons with significantly reduced dendrites. (Q and R) A-type (Q) and sustained (R) K+ currents are qualitatively similar in controls and MN5 with dendritic defects. (S) Activation voltages of transient and sustained K+ currents are not affected by Dscam1 RNAi. Transient K+ current is identical to controls (n = 31), but sustained K+ current displays a larger amplitude in MN5 with defective dendrites (n = 16). (T) Positive phototaxis and negative geotaxis responses (U) are normal after targeted expression of Dscam1 RNAi under the control of C380-GAL4;; Cha-GAL80.