Figure 4.
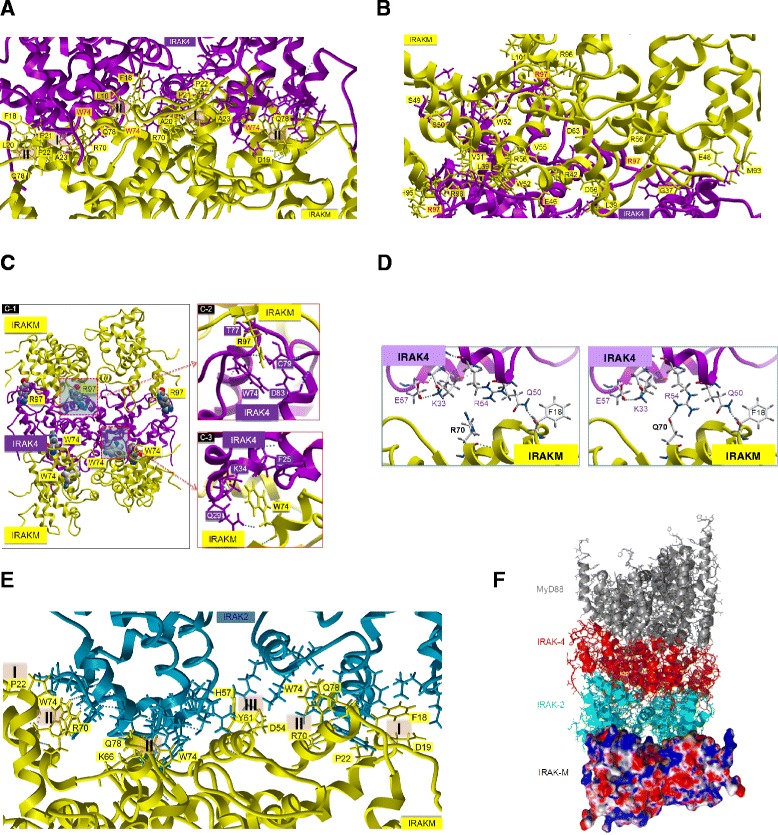
Protein:protein docking of IRAK-M-DD tetramers onto IRAK-4-DD tetramers or IRAK-2-DD tetramers. (A) IRAK-M-DD interactions predicted to be important for the contact between IRAK-M and IRAK-4 as obtained by unbiased docking of the IRAK-M tetramer (Yellow) onto the bottom surface of the IRAK-4 tetramer structure (Purple) as is present in the myddosome (3MOP.pdb also F). The residues involved in the interaction are shown with their side chains, of which the residues from IRAK-M are labeled with their respective residue name and number. Two interaction types were involved (type I residues L20, P21, P22, A23, R70, type II residues L16, F18, W74, S75, Q78). This orientation was observed for 63% of the 100 best docked events. (B) IRAK-M-DD interactions predicted to be important for the contact between IRAK-M and IRAK-4 as obtained by unbiased docking of the IRAK-M tetramer (Yellow) on the top surface of IRAK-4 tetramer (Purple). The residues involved in the interaction are shown with their side chains, including R97. This orientation was observed for 37% of the 100 best docked events. (C) Potential sandwich of one IRAK-4-DD tetramer in between 2 IRAK-M-DD tetramers by W74 and R97 mediated interactions. The respective predicted IRAK-4 interactions are shown in detail. (D) Docking of mutant IRAK-M-DD predicts increased IRAK-4 interaction with the IRAK-M R70Q mutant through an extra hydrogen bond formed between Q70 in IRAK-M and R54 in IRAK-4. (E) Part of the composite binding site of the free side of the IRAK-2-DD tetramer in the myddosome is shown with three IRAK-M-DD molecules. The contact residues are shown with their side chain. The residues involved in the interaction from IRAK-M are labeled. Three interaction types were involved. F) A proposed whole myddosome structure with IRAK-M-DD tetramer docked on the free side of the IRAK-2-DD tetramer, based on the myddosome structure, 3MOP.pdb.
