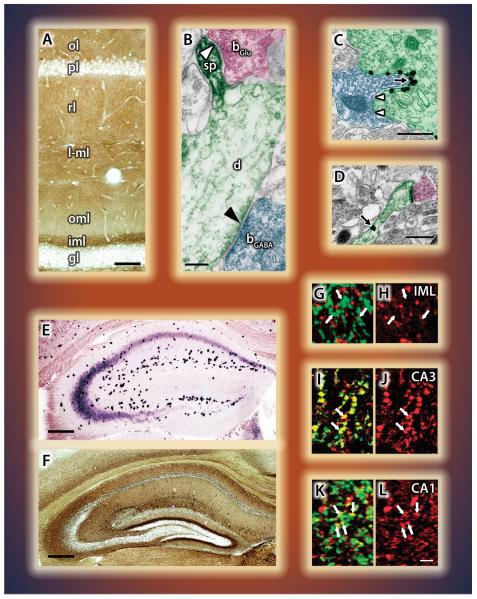
Figure 4. Quantitatively differential distribution of the molecular players of retrograde 2-AG signaling in cortical areas.
A) Laminar distribution of DGL-α in association with glutamatergic synapses in the hippocampus (Katona et al., 2006) and B) in the neocortex (courtesy of Barna Dudok). C,D) In the amygdala, high density of DGL-α occurs at invaginating - but not at flat - GABAergic synapses (C) as well as at glutamatergic (D) axospinous contacts (Yoshida et al., 2011). E) In situ hybridization in the hippocampus reveals high levels of CB1 mRNA in interneurons, lower levels in CA3, and even lower in CA1 pyramidal cells. Dentate granule cells are devoid of labeling. F) Immunostaining for the CB1 receptor protein reveals a striking laminar pattern associated with both GABAergic and glutamatergic terminals (Katona et al., 2006). G-L) Great variability in MGL content between glutamatergic pathways is revealed by double-labeling for vGluT1 (green) and MGL (red). No co-localization in the dentate inner molecular layer (G,H), but a high degree of overlap in recurrent axon terminals in CA3 (I,J), and moderate co-localization in Schaffer collateral terminals in CA1 (K,L) (Uchigashima et al., 2011). The individual figures have been modified from the originals with permission from the authors.