Figure 5.
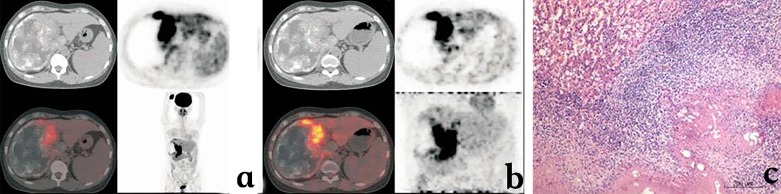
18F-Fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) Positron-emission tomography (PET) aspects of hepatic alveolar echinococcosis. (a) Early image acquisition (1 hour after FDG injection): large-sized heterogeneous space-occupying lesion in the right lobe of the liver, with multiple scattered calcifications and areas of liquefaction necrosis, without obvious FDG uptake inside the lesion; significant FDG uptake at the border of the lesion, at the junction of the right and left lobes, irregular in shape. (b) Delayed image acquisition (3 hours after FDG injection): significantly enhanced images of FDG uptake, with an increase in SUV value. (c) Pathology of the HAE lesion sampled in the area of high FDG uptake: fibroblast proliferation, associated with macrophage, lymphocyte, plasma cell, and eosinophil-rich inflammatory infiltrate.
