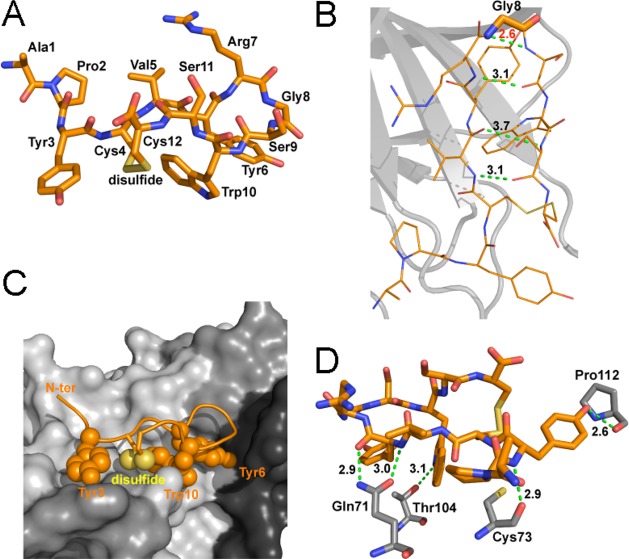
Figure 2.
Detailed structure of APY bound to EphA4. (A) Detailed view of the structure of the APY peptide, which is shown in stick representation in orange with oxygens in red, nitrogens in blue, and disulfide bond in yellow. (B) The APY peptide has three intramolecular hydrogen bonds (dotted green lines, with distance in Å shown in black). The β-turn around Gly8 (indicated with thicker sticks) shows high strain, as indicated by the short unfavorable N–N distance between the Gly and Ser9 (dotted green line, with distance in Å shown in red). APY molecule A is shown, with all four molecules in the asymmetric unit shown in Supporting Information Figure 3. (C) The APY peptide is shown within the ephrin-binding pocket of EphA4. The hydrophobic peptide residues interacting with EphA4 are shown as spheres. EphA4 is shown in surface representation in gray with the DE, GH, and JK loops in darker shades of gray. N-ter, N-terminus. (D) There are five hydrogen bonds (dotted green lines, with distances in Å shown in black) between residues in APY (orange) and EphA4 (gray). Only EphA4 residues engaged in hydrogen bonds are shown.