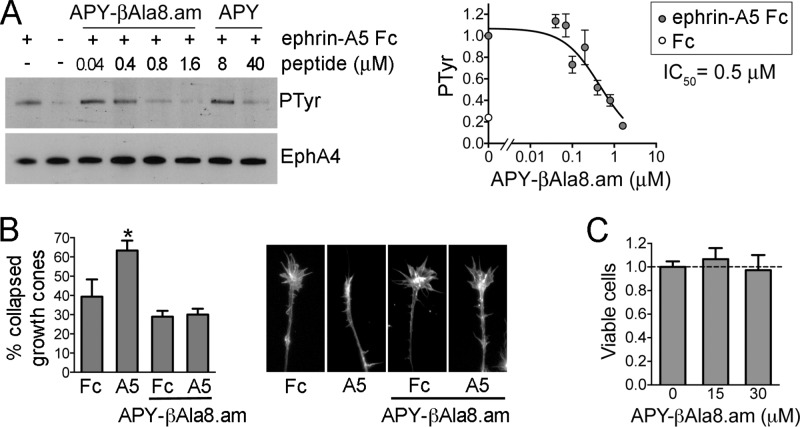
Figure 5.
Inhibition of EphA4 activation in cells by APY-βAla8.am. (A) Inhibition of ephrin-A5-induced EphA4 tyrosine phosphorylation. EphA4 was immunoprecipitated from stably transfected HEK293 cells treated with ephrin-A5 Fc (+) or Fc control (−) in the presence of the indicated concentrations of APY-βAla8.am or APY. The immunoprecipitates were probed for phosphotyrosine (PTyr) and reprobed for EphA4. The graph on the right shows quantification of EphA4 tyrosine phosphorylation levels from the immunoblots of seven experiments, normalized to the phosphorylation level in the ephrin-A5/no peptide condition in each experiment. Averages from three to six measurements ± SE are shown in the graph. (B) Inhibition of EphA4-dependent growth cone collapse. Explants from embryonic day 6 chicken retina were pretreated with 0.3 μM APY-βAla8.am peptide, stimulated with ephrin-A5 Fc or Fc as a control, and stained to label actin filaments. The histogram shows the mean percentages of collapsed growth cones (∼70 to 500 per condition in each experiment). Error bars represent standard errors from three experiments. *, P < 0.05 compared to Fc without peptide by one-way ANOVA. (C) The APY-βAla8.am peptide does not have detectable cytotoxic effects. HT22 neuronal cells were grown in the presence of 30 μM peptide, or without peptide as a control, for 24 h, and cell viability was assessed using the MTT assay. Averages from six measurements ± SE are shown.