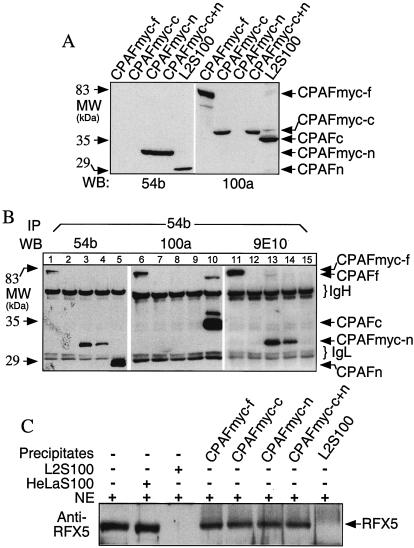
FIG. 4.
Transgene-encoded CPAF or CPAF fragments failed to form dimers and to degrade RFX5. 293T cells were transfected with plasmids coding for the full-length protein (CPAFmyc), the C terminus (CPAFmyc-c), or the N terminus (CPAFmyc-n) or were cotransfected with both the C terminus plasmid and the N terminus plasmid (CPAFmyc-c+n). (A) Cell lysates from the transfectants or chlamydia-infected cells (L2S100 was a positive control) were subjected to Western blot analysis with either the N-terminus-specific MAb 54b or the C-terminus-specific MAb 100a. (B) Alternatively, all the cell lysates were precipitated with MAb 54b, and the precipitated pellets were then subjected to Western blot analysis with MAb54b, 100a, or 9E10 (anti-myc tag). Lanes 1, 6, and 11, cells transfected with CPAFmyc-f plasmid; lanes 2, 7, and 12, cells transfected with CPAFmyc-c plasmid; lanes 3, 8, and 13, cells transfected with CPAFmyc-c plasmid; lanes 4, 9, and 14, cells transfected with CPAFmyc-c+n plasmids; lanes 5, 10, and 15, chlamydia-infected cells (L2S100). (C) The precipitates described above were also used to degrade RFX5 in a cell-free degradation assay. Molecular masses (MW) are indicated on the left, while the positions of protein bands are indicated on the right. IgH, immunoglobulin heavy chains; IgL, immunoglobulin light chains; IP, immunoprecipitation; WB, Western blot; NE, nuclear extracts (as the source of RFX5).