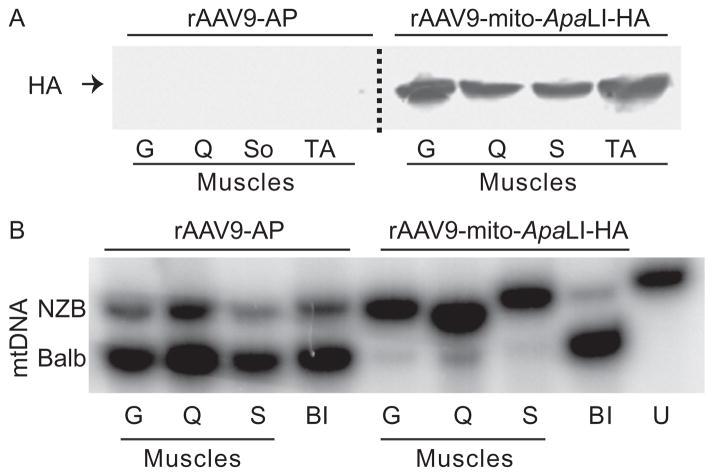
Figure 18.3.
Recombinant rAAV9-mito-ApaLI-HA induces a shift in mtDNA heteroplasmy in muscle. Neonatal mice heteroplasmic for the mtDNA haplotypes NZB and BALB were injected i.p. with rAAV9 expressing either a control alkaline phosphatase (AP) or a mito-ApaLI-HA. (A) The expression of ApaLI-HA was analyzed by anti-HA Western blotting 6 weeks after i.p. injections in P2–P3 mice. Homogenates from different skeletal muscles showed expression. (B) NZB/BALB mtDNA heteroplasmy quantified using last-cycle hot PCR/RFLP with DNA samples from mice injected with rAAV9-mito-ApaLI-HA at 6 weeks i.p. postinjections. Increases in the percentage of NZB mtDNA were observed in all skeletal muscle when compared to the samples obtained from the tail before injection. Gastrocnemius (G), quadriceps (Q), soleus (S), tibialis anterior (TA), before injection (BI), and uncut DNA (U). Adapted from Bacman et al. (2012). (See the color plate.)