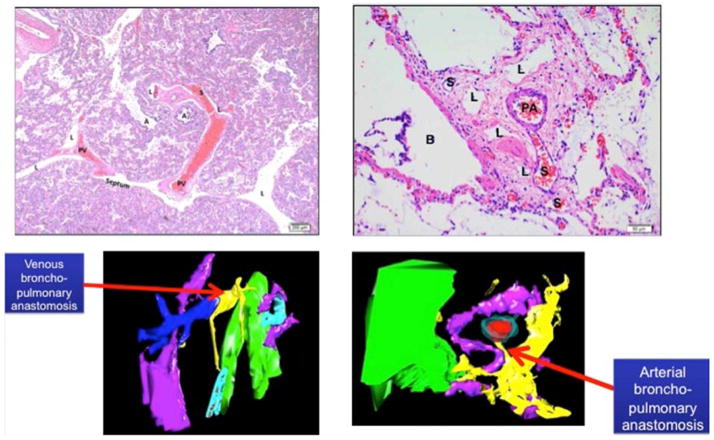
Figure 3.
Venous Intrapulmonary anastomotic vessels (IPAV) (or shunt vessels; designated as “S”) are recognized as thin walled vessels that bridge pulmonary veins and microvessels surrounding pulmonary arteries and airways (top left panel). Arterial IPAV are connections between PA and BA (upper right panel) Lower panels show 3D reconstruction images of venous (left bottom) and arterial (right bottom) bronchopulmonary anastomotic or “shunt” vessels (yellow). (Color key: yellow: shunt vessel; red: PA endothelium; aqua; PA wall; pink: lymphatic; green: airway). Abbreviations: S, shunt vessel; A, airspace; PV, pulmonary vein; L lymphatic; PA, pulmonary artery; B, bronchus).