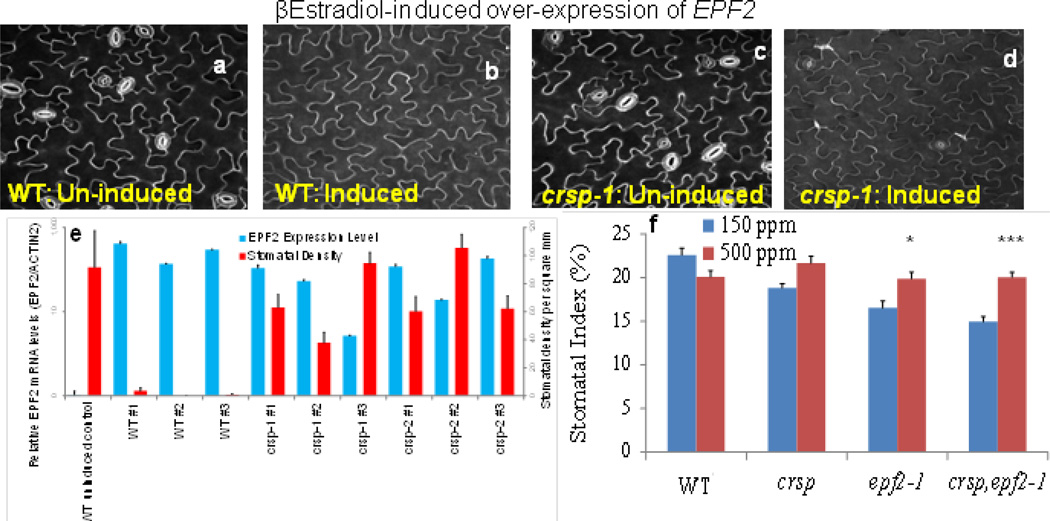
Extended Data Figure 7. CRSP is required for EPF2 function in planta and CO2 control of stomatal development in crsp epf2 double mutant plants.
a–d, WT and crsp mutant seedlings harbouring an oestradiol-inducible EPF2 construct were germinated in the absence (uninduced; a and c) or presence (induced; b and d) of β-oestradiol. The cotyledon epidermis of 5-day-old seedlings was imaged using a confocal microscope and propidium iodide staining. e, Quantitation of the effects of EPF2 transcript levels on 5-day-old cotyledon stomatal density (number of stomata per mm2) in nine independent lines harbouring the β-oestradiol-inducible EPF2 overexpression construct in the WT, crsp-1 or crsp-2 mutant backgrounds and the WT control (uninduced). For each line, 20 images from 10 cotyledons (2 images per cotyledon; 10 separate seedlings used) were analysed, and RNA was extracted from 10 separate seedlings (see Methods). f, Abaxial stomatal indices for mature cotyledons (10 DAG) of WT (Col), the crsp-1 and epf2-1 single mutants, and the crsp-1 epf2-1 double mutant plants grown at low (blue) and high (red) CO2 concentrations. SLGCs are included in these stomatal index (SI) calculations. n = 20 in e and f. In f, ***, P< 0.00005;*, P < 0.05, using ANOVA and Tukey’s post-hoc test. Error bars, mean ± s.e.m.