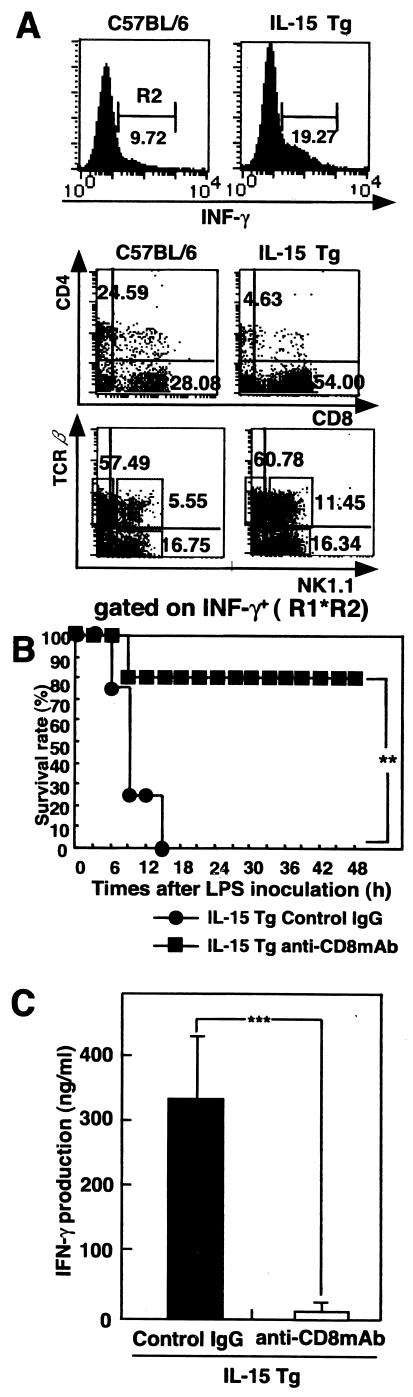
FIG. 3.
CD8+ T cells are responsible for LPS-induced lethal shock in BCG-primed IL-15 Tg mice. (A) BCG-primed IL-15 Tg mice and control C57BL/6 mice were i.v. injected with LPS, and liver mononuclear cells were harvested 3 h later. Cytokine FACS analysis was carried out for the expression of CD4, CD8, and intracellular IFN-γ or for NK1.1, TCRαβ, and intracellular IFN-γ. The results of flow cytometry are presented as typical profiles after an analysis gate had beenset on lymphocytes using forward and side scatter (R1 data not shown) and on IFN-γ+ cells (R2). (B) Effect of depletion of CD8+ T cells on survival rate after LPS injection of BCG-primed IL-15 Tg mice. BCG-primed IL-15 Tg mice were i.p. injected with anti-CD8 MAb or control IgG 24 h before LPS inoculation. After CD8+ T cell depletion, mice were i.v. injected with 10 μg LPS. **, significantly different from the value for control mice (P value of <0.01 by the generalized Wilcoxon test). Seven to 10 mice per group were used per experiment. The typical results of one of three independent experiments are shown. (C) Effect of depletion of CD8+ T cells on IFN-γ production after LPS injection in BCG-primed IL-15 Tg mice. IL-15 Tg mice were treated i.p. with anti-CD8 MAb or control IgG 24 h before LPS injection. Sera were collected at 6 h after LPS challenge from Ab-treated mice. IFN-γ levels in serum after LPS challenge in BCG-primed IL-15 Tg mice are shown. Data are presented as the means + SDs for five mice. ***, P < 0.001.