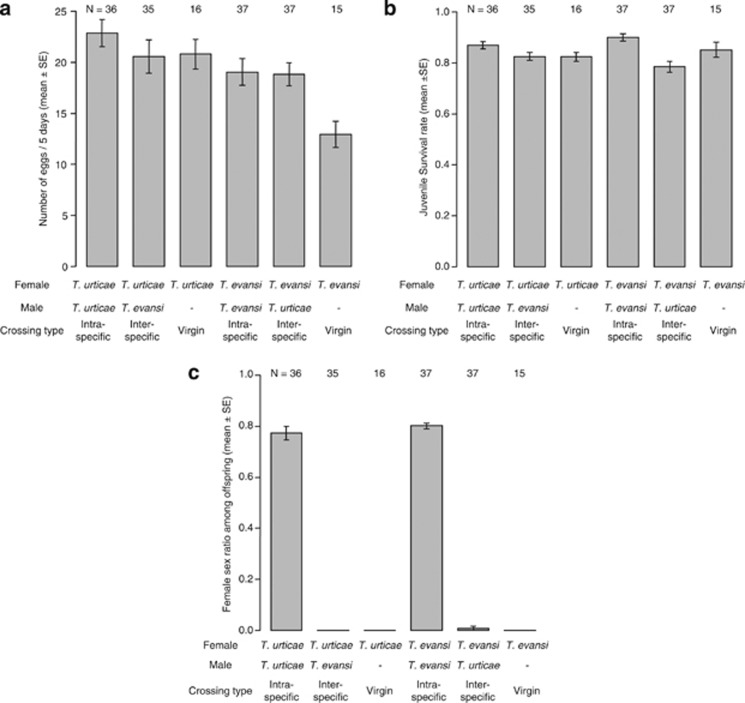
Figure 4.
Bar plots of (a) the number of eggs, (b) the juvenile survival rate of offspring and (c) the female sex ratio among offspring produced by females mated with conspecific or heterospecific males or by virgin females. Column bars express means and vertical line bars represent standard errors. The effect of crossing type on the number of eggs was not significant (two-way ANOVA, crossing type: F1,142=0.83, P=0.36, female species: F1,142=4.33, P=0.039). However, the effect of crossing type on the juvenile survival rate of offspring was bordering significance (likelihood ratio test, cross type: χ2=3.68, P=0.06, female species: χ2=0.003, P=0.96), and the effect of crossing type on the sex ratio of offspring was significant (likelihood ratio test, cross type: χ2=983.19, P<0.001, female species: χ2=0.16, P=0.69).