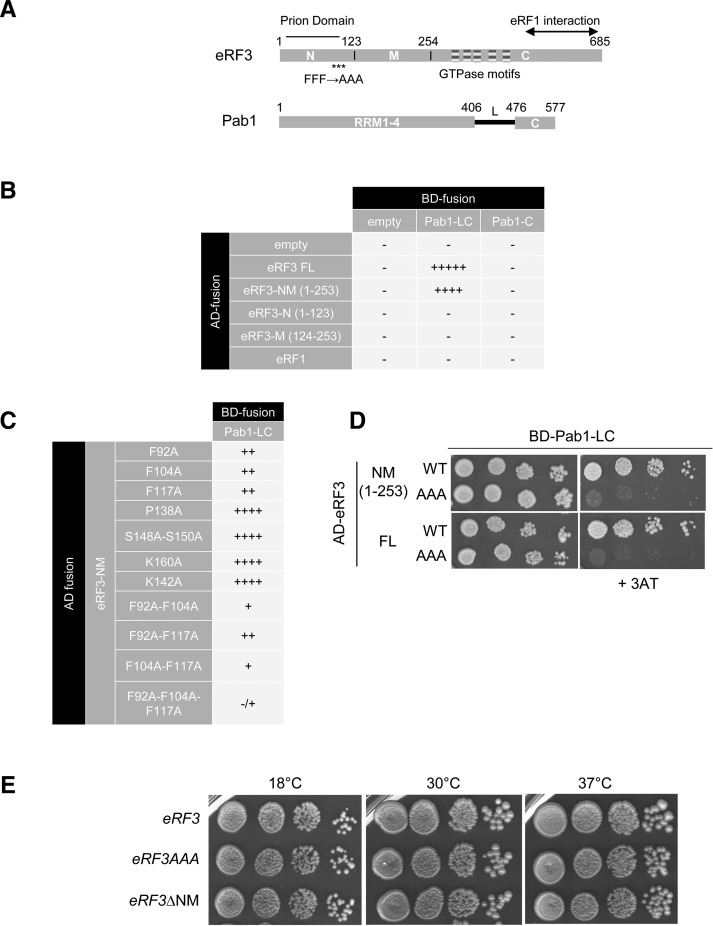
FIGURE 1.
Interaction between Pab1 and eRF3 in the two-hybrid reporter system. (A) Schematic representation of eRF3 and Pab1 functional domains. The eRF3 GTPase motifs are represented by striped boxes. Prion determinant and eRF1 interacting region are depicted. The asterisks indicate the location of the three mutated phenylalanine residues. (B) Identification of the eRF3 interacting domains with Pab1 in the two-hybrid reporter system. The fusion GAL4-AD-eRF1 was used as a negative control. The interaction was analyzed by scoring the growth on the appropriate medium after 6 d at 30°C; (−) no growth in absence of 3AT, (−/+) no growth on 1 mM 3AT, (+) no growth on 5 mM 3AT, (++) no growth on 10 mM 3AT, (++++) growth on 10 mM 3AT, (+++++) growth on 20 mM 3AT. (C) Mutations of eRF3-NM domain. The indicated mutations were introduced and the interaction with Pab1-LC domain was tested as described for B. (D) Mutation of phenylalanine residues in alanine at position 92, 140, and 117 affects eRF3 interaction with Pab1. Interaction of Pab1-LC domain with full length (FL) or the NM domain of eRF3 either wild-type (WT) or harboring the triple mutation (AAA) was analyzed by serially diluting and spotting the reporter strain expressing the different construction on selective medium containing 3AT (right panel). Growth was scored after 5 d of growth at 30°C. (E) Growth phenotype of eRF3 mutant strains. The indicated strains (SKY1085, SKY1081, and SKY1182) were grown overnight in YPDA at 30°, serially diluted and spotted onto YPDA plate. Growth was scored after 3 d of growth at 30°C and 37°C, and 4 d at 18°C.