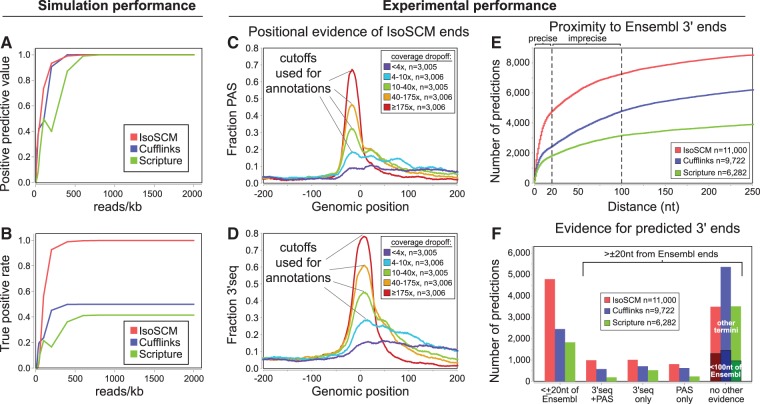
FIGURE 3.
Comparison of IsoSCM with existing transcript assembly methods. (A,B) Simulated RNA-seq data were used to assess predictive positive value (A) and true positive rate (B) of IsoSCM, Cufflinks, and Scripture outputs for 3′ end prediction. We generated a set of 14,263 nonoverlapping gene models that contain transcripts with nested 3′ terminal exons, and used these as a reference set of “true” transcripts. These metrics were calculated for simulated sequencing depths ranging from 5 to 2000 reads/kb. (C,D) We assessed the positional accuracy of IsoSCM outputs across a range of change-point magnitudes. We partitioned these events into quintiles (with n = 3005 termini in each group), corresponding to bins of <4x, 4–10x, 10–40x, 40–175x, and ≥175x drop-offs in read coverage. For each group the fraction of predicted termini with either canonical polyadenylation signals (PAS, AATAAA, or ATTAAA) or 3′-seq tags within 20 nt are shown at each position relative to the predicted boundary. Based on signals for appropriate positional enrichment, we utilized the top four cutoffs for running IsoSCM. (E) Proximity of IsoSCM, Cufflinks, and Scripture terminal outputs relative to Ensembl 3′ end annotations. The cumulative number of annotations at each distance to the closest Ensembl 3′ end is plotted. Based on apparent inflection points (dashed lines), we categorize annotations within 20 nt of Ensembl as precise annotations, and ones between 20 and 100 nt as imprecise matches to reference models. (F) Validation of IsoSCM, Cufflinks, and Scripture terminal outputs within ±20-nt windows of various types of supporting evidence. Ends were initially assigned, if possible, to Ensembl models, and then checked for proximity to PAS and/or 3′-seq tags. Of the remaining termini with “no evidence,” many would be validated using a relaxed 100-nt window. As the largest numbers of these correspond to “imprecise” calls of Ensembl ends (see E), we marked their numbers as sub-bars in the “no evidence” category. Regardless of the type or types of evidence considered, IsoSCM yields the largest numbers of validated termini without inflating numbers of unvalidated predictions.